Dibenzothiophene: Difference between revisions
حسن علي البط (talk | contribs) m Removed Category:Thioethers (using HotCat) |
→Synthesis and reactions: electron-poor/rich |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{Chembox |
||
| Watchedfields = changed |
|||
| verifiedrevid = |
| verifiedrevid = 443634616 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| Name = Dibenzothiophene |
||
| ImageFile = Dibenzothiophen - Dibenzothiophene.svg |
|||
| ImageSize = 190px |
| ImageSize = 190px |
||
| ImageName = Skeletal formula |
|||
| ImageAlt = Skeletal formula of dibenzothiophene |
|||
| ImageFile1 = Dibenzothiophene-3D-balls.png |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ImageSize1 = 230px |
|||
| ImageSize1 = 220px |
|||
| ImageName1 = Ball-and-stick model |
|||
| ImageAlt1 = Ball-and-stick model of the dibenzothiophene molecule |
|||
| IUPACName = Dibenzothiophene |
|||
| ImageFile2 = DBTsample.jpg |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ImageSize2 = 180px |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| ImageAlt2 = Sample |
||
| PIN = Dibenzo[''b'',''d'']thiophene |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
|||
| ChEBI = 23681 |
|||
| SMILES = c1ccc2c(c1)c3ccccc3s2 |
|||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| ChemSpiderID = 2915 |
|||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
|||
| UNII = Z3D4AJ1R48 |
|||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} |
|||
| KEGG = D03777 |
|||
| InChI = 1/C12H8S/c1-3-7-11-9(5-1)10-6-2-4-8-12(10)13-11/h1-8H |
|||
| InChIKey = IYYZUPMFVPLQIF-UHFFFAOYAY |
|||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
|||
| ChEMBL = 219828 |
|||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChI = 1S/C12H8S/c1-3-7-11-9(5-1)10-6-2-4-8-12(10)13-11/h1-8H |
|||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChIKey = IYYZUPMFVPLQIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| CASNo = 132-65-0 |
| CASNo = 132-65-0 |
||
| |
| RTECS = HQ3490550 |
||
| PubChem = 3023 |
|||
| EC_number = 205-072-9 |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| Section2 = {{Chembox Properties |
| Section2 = {{Chembox Properties |
||
| |
| Formula = C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>8</sub>S |
||
| |
| MolarMass = 184.26 g/mol |
||
| |
| Appearance = Colourless crystals |
||
| |
| Density = 1.252 g/cm<sup>3</sup> |
||
| |
| Solubility = insol. |
||
| |
| Solvent = other solvents |
||
| |
| SolubleOther = [[benzene]] and related |
||
| |
| MeltingPtC = 97 to 100 |
||
| MeltingPt_notes = (lit.) |
|||
| BoilingPt = 332-333 °C |
|||
| |
| BoilingPtC = 332 to 333 |
||
| BoilingPt_notes = |
|||
| pKb = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| Section3 = {{Chembox Structure |
| Section3 = {{Chembox Structure |
||
| |
| CrystalStruct = |
||
| |
| Dipole = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards |
| Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards |
||
| |
| ExternalSDS = |
||
| |
| MainHazards = flammable, toxic |
||
| |
| FlashPt = |
||
| GHSPictograms = {{GHS skull and crossbones}}{{GHS exclamation mark}}{{GHS environment}} |
|||
| RPhrases = 22 |
|||
| |
| GHSSignalWord = Danger |
||
| HPhrases = {{H-phrases|301|302|311|315|331|332|410}} |
|||
| PPhrases = {{P-phrases|261|264|270|271|273|280|301+312|302+352|304+312|304+340|311|312|321|322|330|332+313|361|362|363|391|403+233|405|501}} |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| Section8 = {{Chembox Related |
| Section8 = {{Chembox Related |
||
| |
| OtherCompounds = [[Thiophene]]<br/>[[Anthracene]]<br/>[[Benzothiophene]]<br/>[[Dibenzofuran]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Dibenzothiophene is the [[organosulfur compound]] consisting of two benzene |
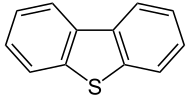
'''Dibenzothiophene''' (DBT, diphenylene [[Sulfide (organic)|sulfide]]) is the [[organosulfur compound]] consisting of two [[benzene ring]]s fused to a central [[thiophene]] ring. It has the chemical formula C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>8</sub>S. It is a colourless solid that is chemically somewhat similar to [[anthracene]]. This [[tricyclic]] [[heterocyclic compound|heterocycle]], and especially its disubstituted derivative [[4,6-Dimethyldibenzothiophene|4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene]] are problematic impurities in [[petroleum]].<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1016/j.cattod.2004.07.048|title=Deep HDS of Diesel Fuel: Chemistry and Catalysis |year=2004 |last1=Ho |first1=Teh C. |journal=Catalysis Today |volume=98 |issue=1–2 |pages=3–18 }}</ref> |
||
==Synthesis and reactions== |
==Synthesis and reactions== |
||
Dibenzothiophene is prepared by the reaction of [[biphenyl]] with [[sulfur dichloride]] in the presence of [[aluminium |
Dibenzothiophene is prepared by the reaction of [[biphenyl]] with [[sulfur dichloride]] in the presence of [[aluminium chloride]].<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1002/jhet.5570150407|title=The Insertion and Extrusion of Heterosulfur Bridges. VIII. Dibenzothiophene from Biphenyl and Derivatives |year=1978 |last1=Klemm |first1=L. H. |last2=Karchesy |first2=Joseph J. |journal=Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry |volume=15 |issue=4 |pages=561–563 }}</ref> |
||
Reduction with [[lithium]] results in scission of one C-S bond. With [[butyllithium]], this heterocycle undergoes stepwise lithiation at the 4-position. S-oxidation with peroxides gives the [[sulfoxide]].<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.15227/orgsyn.096.0258|title=Preparation of 5-(Triisopropylalkynyl) dibenzo[b,d]thiophenium triflate |year=2019 |last1=Waldecker |first1=Bernd |journal=Organic Syntheses |volume=96 |pages=258–276 |s2cid=239319277|first2= Kevin|last2=Kafuta|first3=Manuel|last3=Alcarazo|doi-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
Reduction with lithium results in scission of one C-S bond. S-oxidation occurs to give the [[sulfone]], which is more labile than the parent dibenzothiophene. With [[butyl lithium]], this heterocycle undergoes stepwise lithiation at the 4- and 6- positions. |
|||
Dibenzothiophene is [[electron-rich]], and naturally undergoes aromatic substitution [[arene substitution patterns|''para'']] to the sulfide. Oxidation to the sulfoxide or sulfone leaves the compound electron poor, and substitution occurs at the ''meta'' position instead.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis|doi=10.1002/047084289X.rn02046|entry=Dibenzothiophene 5,5-dioxide|first1=M.|last1=Bhanuchandra|author2=Yorimitsu Hideki}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<references/> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[ca:Dibenzotiofè]] |
|||
[[es:Dibenzotiofeno]] |
|||
[[fr:Dibenzothiophène]] |
|||
[[ja:ジベンゾチオフェン]] |
|||
[[pl:Dibenzotiofen]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 00:38, 8 July 2024
| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dibenzo[b,d]thiophene | |
| Other names
Diphenylene sulfide, DBT
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.613 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H8S | |
| Molar mass | 184.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless crystals |
| Density | 1.252 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 97 to 100 °C (207 to 212 °F; 370 to 373 K) (lit.) |
| Boiling point | 332 to 333 °C (630 to 631 °F; 605 to 606 K) |
| insol. | |
| Solubility in other solvents | benzene and related |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
flammable, toxic |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H302, H311, H315, H331, H332, H410 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P361, P362, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Thiophene Anthracene Benzothiophene Dibenzofuran |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dibenzothiophene (DBT, diphenylene sulfide) is the organosulfur compound consisting of two benzene rings fused to a central thiophene ring. It has the chemical formula C12H8S. It is a colourless solid that is chemically somewhat similar to anthracene. This tricyclic heterocycle, and especially its disubstituted derivative 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene are problematic impurities in petroleum.[1]
Synthesis and reactions
[edit]Dibenzothiophene is prepared by the reaction of biphenyl with sulfur dichloride in the presence of aluminium chloride.[2]
Reduction with lithium results in scission of one C-S bond. With butyllithium, this heterocycle undergoes stepwise lithiation at the 4-position. S-oxidation with peroxides gives the sulfoxide.[3]
Dibenzothiophene is electron-rich, and naturally undergoes aromatic substitution para to the sulfide. Oxidation to the sulfoxide or sulfone leaves the compound electron poor, and substitution occurs at the meta position instead.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Ho, Teh C. (2004). "Deep HDS of Diesel Fuel: Chemistry and Catalysis". Catalysis Today. 98 (1–2): 3–18. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2004.07.048.
- ^ Klemm, L. H.; Karchesy, Joseph J. (1978). "The Insertion and Extrusion of Heterosulfur Bridges. VIII. Dibenzothiophene from Biphenyl and Derivatives". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry. 15 (4): 561–563. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570150407.
- ^ Waldecker, Bernd; Kafuta, Kevin; Alcarazo, Manuel (2019). "Preparation of 5-(Triisopropylalkynyl) dibenzo[b,d]thiophenium triflate". Organic Syntheses. 96: 258–276. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.096.0258. S2CID 239319277.
- ^ Bhanuchandra, M.; Yorimitsu Hideki. "Dibenzothiophene 5,5-dioxide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn02046.
