Coronavirus
It has been suggested that this article be merged into Orthocoronavirinae. (Discuss) Proposed since January 2019. |
| Coronavirus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group IV ((+)ssRNA)
|
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | |
| Type species | |
| Coronavirus | |
| Species | |
Coronaviruses are species of virus belonging to the subfamily Coronavirinae in the family Coronaviridae, in the order Nidovirales.[1][2] Coronaviruses are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and with a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genomic size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, the largest for an RNA virus.
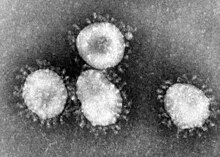
The name "coronavirus" is derived from the Latin corona, meaning crown or halo, and refers to the characteristic appearance of virions (the infective form of the virus) under electron microscopy (E.M.) with a fringe of large, bulbous surface projections creating an image reminiscent of a royal crown or of the solar corona. This morphology is created by the viral spike (S) peplomers, which are proteins that populate the surface of the virus and determine host tropism.
Proteins that contribute to the overall structure of all coronaviruses are the spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M) and nucleocapsid (N). In the specific case of the SARS coronavirus (see below), a defined receptor-binding domain on S mediates the attachment of the virus to its cellular receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).[3] Some coronaviruses (specifically the members of Betacoronavirus subgroup A) also have a shorter spike-like protein called hemagglutinin esterase (HE).[1]
History
Coronaviruses were first described in the 1960s from the nasal cavities of patients with the common cold. These viruses were subsequently named human coronavirus 229E and human coronavirus OC43.[4] Two further members of this family have been identified (HCoV NL63 in 2004 and HKU1 in 2005) and they have been involved in more serious respiratory tract infections. As of January 2020, deaths from China have risen to 17 with more than 540 cases confirmed. It is suspected to originate from illegally-traded wildlife.
Coronaviruses primarily infect the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tract of mammals and birds. Currently there are seven known strains of Coronaviruses that infect humans. Coronaviruses are believed to cause a significant percentage of all common colds in human adults and children. Coronaviruses cause colds with major symptoms, e.g. fever, throat swollen adenoids, in humans primarily in the winter and early spring seasons.[5] Coronaviruses can cause pneumonia, either direct viral pneumonia or a secondary bacterial pneumonia, and bronchitis, either direct viral bronchitis or a secondary bacterial bronchitis.[6] The much publicized human coronavirus discovered in 2003, SARS-CoV which causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), has a unique pathogenesis because it causes both upper and lower respiratory tract infections.[6] The significance and economic impact of coronaviruses as causative agents of the common cold are hard to assess because, unlike rhinoviruses (another common cold virus), human coronaviruses are difficult to grow in the laboratory.
Coronaviruses also cause a range of diseases in farm animals and domesticated pets, some of which can be serious and are a threat to the farming industry. In chickens, the infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), a coronavirus, targets not only the respiratory tract but also the urogenital tract. The virus can spread to different organs throughout the chicken.[7] Economically significant coronaviruses of farm animals include porcine coronavirus (transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus, TGE) and bovine coronavirus, which both result in diarrhea in young animals. Feline coronavirus: two forms, feline enteric coronavirus is a pathogen of minor clinical significance, but spontaneous mutation of this virus can result in feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), a disease associated with high mortality. Similarly, there are two types of coronavirus that infect ferrets: ferret enteric coronavirus causes a gastrointestinal syndrome known as epizootic catarrhal enteritis (ECE), and a more lethal systemic version of the virus (like FIP in cats) known in ferrets as ferret systemic coronavirus (FSC).[8] There are two types of canine coronavirus (CCoV), one that causes mild gastrointestinal disease and one that has been found to cause respiratory disease. Mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) is a coronavirus that causes an epidemic murine illness with high mortality, especially among colonies of laboratory mice.[9]
A HKU2-related bat coronavirus called swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus (SADS-CoV) causes diarrhea in pigs.[10]
Prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV, MHV had been the best-studied coronavirus both in vivo and in vitro as well as at the molecular level. Some strains of MHV cause a progressive demyelinating encephalitis in mice which has been used as a murine model for multiple sclerosis. Significant research efforts have been focused on elucidating the viral pathogenesis of these animal coronaviruses, especially by virologists interested in veterinary and zoonotic diseases.[11]
Replication

Replication of coronavirus begins with entry into the cell. Upon entry into the cell, the virus particle is uncoated and the RNA genome is deposited into the cytoplasm.
The coronavirus RNA genome has a 5′ methylated cap and a 3′polyadenylated tail. This allows the RNA to attach to ribosomes for translation.
Coronaviruses also have a protein known as a replicase encoded in its genome which allows the RNA viral genome to be transcribed into new RNA copies using the host cell's machinery. The replicase is the first protein to be made; once the gene encoding the replicase is translated, the translation is stopped by a stop codon. This is known as a nested transcript. When the mRNA transcript only encodes one gene, it is monocistronic. A coronavirus non-structural protein provides extra fidelity to replication because it confers a proofreading function,[12] which is lacking in RNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzymes alone.
The RNA genome is replicated and a long polyprotein is formed, where all of the proteins are attached. Coronaviruses have a non-structural protein – a protease – which is able to separate the proteins in the chain. This is a form of genetic economy for the virus, allowing it to encode the greatest number of genes in a small number of nucleotides.[13]
There are seven known strains of human coronaviruses:
- Human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E)
- Human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43)
- SARS-CoV
- Human coronavirus NL63 (HCoV-NL63, New Haven coronavirus)
- Human coronavirus HKU1
- Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), previously known as Novel coronavirus 2012 and HCoV-EMC.
- Wuhan coronavirus (2019-nCoV),[14][15] also known as novel coronavirus 2019/2020 (Wuhan pneumonia).[16]
Following the high-profile publicity of SARS outbreaks in 2003, there has been a renewed interest in coronaviruses among virologists. For many years, scientists knew about only two human coronaviruses (HCoV-229E and HCoV-OC43). The discovery of SARS-CoV added a third human coronavirus.
By the end of 2004, three independent research labs reported the discovery of a fourth human coronavirus. It has been named NL63, NL, and the New Haven coronavirus by different research groups.[17] The three labs are still arguing over which one discovered the virus first and who has the right to name it.
Early in 2005, a research team at the University of Hong Kong reported finding a fifth human coronavirus in two patients with pneumonia. They named it Human coronavirus HKU1.
The 2019–20 China pneumonia outbreak in Wuhan was traced to a novel coronavirus,[18] which is labeled as 2019-nCoV by WHO.[14][15]
Severe acute respiratory syndrome
In 2003, following the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) which had begun the prior year in Asia, and secondary cases elsewhere in the world, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued a press release stating that a novel coronavirus identified by a number of laboratories was the causative agent for SARS. The virus was officially named the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV).
Over 8,000 people were infected, about 10% of whom died.[3]
Middle East respiratory syndrome
In September 2012, a new type of coronavirus was identified, initially called Novel Coronavirus 2012, and now officially named Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).[19][20]
The World Health Organization issued a global alert soon after.[21] The WHO update on 28 September 2012 stated that the virus did not seem to pass easily from person to person.[22] However, on 12 May 2013, a case of human to human transmission in France was confirmed by the French Ministry of Social Affairs and Health.[23] In addition, cases of human to human transmission have been reported by the Ministry of Health in Tunisia. Two confirmed cases seem to have caught the disease from their late father, who became ill after a visit to Qatar and Saudi Arabia. Despite this, it appears that the virus has trouble spreading from human to human, as most individuals who are infected do not transmit the virus.[24]
By 30 October 2013, there were 124 cases and 52 deaths in Saudi Arabia.[25] After the Dutch Erasmus Medical Centre sequenced the virus, the virus was given a new name, Human CoronaVirus-Erasmus Medical Centre (HCoV-EMC). The final name for the virus is Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
In May 2014, the only two United States cases of MERS-CoV infection were recorded, both occurring in healthcare workers who worked in Saudi Arabia and then traveled to the U.S.. One was treated in Indiana and one in Florida. Both of these individuals were hospitalized temporarily and then discharged.[26]
In May 2015, an outbreak of MERS-CoV occurred in the Republic of Korea, when a man who had traveled to the Middle East, visited 4 different hospitals in the Seoul area to treat his illness. This caused one of the largest outbreaks of MERS-CoV outside of the Middle East.[27]
As of December 2019, 2,468 cases of MERS-CoV infection had been confirmed by laboratory tests, 851 of which were fatal, a mortality rate of approximately 34.5%.[28]
In veterinary medicine
Coronaviruses have been recognized as causing pathological conditions in veterinary medicine since the early 1970s. Except for avian infectious bronchitis, the major related diseases have mainly an intestinal location.
(listed following their estimated economical importance)
- Infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) causes avian infectious bronchitis.
- Porcine coronavirus (transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus of pigs, TGEV).[29][30]
- Bovine coronavirus (BCV), responsible for severe profuse enteritis in of young calves.
- Feline coronavirus (FCoV) causes mild enteritis in cats as well as severe Feline infectious peritonitis (other variants of the same virus).
- the two types of canine coronavirus (CCoV) (one causing enteritis, the other found in respiratory diseases).
- Turkey coronavirus (TCV) causes enteritis in turkeys.
- Ferret enteric coronavirus causes epizootic catarrhal enteritis in ferrets.
- Ferret systemic coronavirus causes FIP-like systemic syndrome in ferrets.[31]
- Pantropic canine coronavirus.
Another new veterinary disease, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PED or PEDV), has emerged around the world. Its economic importance is as yet unclear, but shows high mortality in piglets.
Taxonomy
- Genus: Alphacoronavirus; type species: Alphacoronavirus 1[29][30]
- Genus Betacoronavirus; type species: Murine coronavirus
- Species: Betacoronavirus 1, Human coronavirus HKU1, Murine coronavirus, Pipistrellus Bat coronavirus HKU5, Rousettus Bat coronavirus HKU9, Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus, Tylonycteris Bat coronavirus HKU4, MERS-CoV, Human coronavirus OC43, Hedgehog coronovirus (EriCoV), Wuhan coronavirus (2019-nCoV)
- Genus Gammacoronavirus; type species: Avian coronavirus
- Genus Deltacoronavirus; type species: Bulbul coronavirus HKU11
Evolution
The most recent common ancestor of the coronavirus has been placed at 8000 BC.[32] They may be considerably older than this.
Another estimate places the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of all coronaviruses around 8100 BC.[33] The MRCA of Alphacoronavirus, Betacoronavirus, Gammacoronavirus, and Deltacoronavirus have been placed at about 2400 BC, 3300 BC, 2800 BC and 3000 BC, respectively. It appears that bats and birds, the warm blooded flying vertebrates, are ideal hosts for the coronavirus gene source with bats for Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and birds for Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus, to fuel coronavirus evolution and dissemination.
Bovine coronavirus and canine respiratory coronavirus diverged from a common ancestor in 1951.[34] Bovine coronavirus and human coronavirus OC43 diverged in 1899. Bovine coronavirus diverged from the equine coronavirus species at the end of the 18th century.
Another estimate suggests that human coronavirus OC43 diverged from bovine coronavirus in 1890.[35]
The MRCA of human coronavirus OC43 has been dated to the 1950s.[36]
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus although related to several bat species appears to have diverged from these several centuries ago.[37]
The most closely related bat coronovirus and the SARS coronavirus diverged in 1986.[38]
A path of evolution of the SARS virus and keen relationship with bats have been proposed.[39][40] The authors suggest that the coronaviruses have been coevolved with bats for a long time and the ancestors of SARS virus first infected the species of the genus Hipposideridae, subsequently spread to species of the Rhinolophidae and then to civets and finally to humans.
Alpaca coronavirus and human coronavirus 229E diverged before 1960.[41]
The human coronavirus NL63 and a bat coronovirus shared an MRCA 563 to 822 years ago.[42]
See also
References
- ^ a b de Groot RJ, Baker SC, Baric R, Enjuanes L, Gorbalenya AE, Holmes KV, Perlman S, Poon L, Rottier PJ, Talbot PJ, Woo PC, Ziebuhr J (2011). "Family Coronaviridae". In AMQ King, E Lefkowitz, MJ Adams, EB Carstens (eds.). Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Elsevier, Oxford. pp. 806–828. ISBN 978-0-12-384684-6.
- ^ International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (24 August 2010). "ICTV Master Species List 2009 – v10" (xls).
- ^ a b Li F, Li W, Farzan M, Harrison SC (September 2005). "Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor". Science. 309 (5742): 1864–1868. Bibcode:2005Sci...309.1864L. doi:10.1126/science.1116480. PMID 16166518.
- ^ Geller C, Varbanov M, Duval RE (November 2012). "Human coronaviruses: insights into environmental resistance and its influence on the development of new antiseptic strategies". Viruses. 4 (11): 3044–3068. doi:10.3390/v4113044. PMC 3509683. PMID 23202515.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Liu P, Shi L, Zhang W, He J, Liu C, Zhao C, Kong SK, Loo JF, Gu D, Hu L (November 2017). "Prevalence and genetic diversity analysis of human coronaviruses among cross-border children". Virology Journal. 14 (1): 230. doi:10.1186/s12985-017-0896-0. PMC 5700739. PMID 29166910.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Forgie S, Marrie TJ (February 2009). "Healthcare-associated atypical pneumonia". Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 30 (1): 67–85. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1119811. PMID 19199189.
- ^ Bande F, Arshad SS, Bejo MH, Moeini H, Omar AR (2015). "Progress and challenges toward the development of vaccines against avian infectious bronchitis". Journal of Immunology Research. 2015: 1–12. doi:10.1155/2015/424860. PMC 4411447. PMID 25954763.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Murray, Jerry (16 April 2014). "What's New With Ferret FIP-like Disease?" (xls). Archived from the original on 24 April 2014. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Weiss SR, Navas-Martin S (December 2005). "Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus". Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 69 (4): 635–664. doi:10.1128/MMBR.69.4.635-664.2005. PMC 1306801. PMID 16339739.
- ^ Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin Archived 31 May 2019 at the Wayback Machine, Peng Zhou, Hang Fan, Tian Lan, Xing-Lou Yang, Wei-Feng Shi, Wei Zhang, Yan Zhu, Ya-Wei Zhang, Qing-Mei Xie, Shailendra Mani, Xiao-Shuang Zheng, Bei Li, Jin-Man Li, Hua Guo, Guang-Qian Pei, Xiao-Ping An, Jun-Wei Chen, Ling Zhou, Kai-Jie Mai, Zi-Xian Wu, Di Li, Danielle E. Anderson, Li-Biao Zhang, Shi-Yue Li, Zhi-Qiang Mi, Tong-Tong He, Feng Cong, Peng-Ju Guo, Ren Huang, Yun Luo, Xiang-Ling Liu, Jing Chen, Yong Huang, Qiang Sun, Xiang-Li-Lan Zhang, Yuan-Yuan Wang, Shao-Zhen Xing, Yan-Shan Chen, Yuan Sun, Juan Li, Peter Daszak, Lin-Fa Wang, Zheng-Li Shi, Yi-Gang Tong & Jing-Yun Ma, Nature, 5 April 2018.
- ^ Tirotta E, Carbajal KS, Schaumburg CS, Whitman L, Lane TE (July 2010). "Cell replacement therapies to promote remyelination in a viral model of demyelination". Journal of Neuroimmunology. 224 (1–2): 101–107. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.05.013. PMC 2919340. PMID 20627412.
- ^ Sexton NR, Smith EC, Blanc H, Vignuzzi M, Peersen OB, Denison MR (August 2016). "Homology-Based Identification of a Mutation in the Coronavirus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase That Confers Resistance to Multiple Mutagens". Journal of Virology. 90 (16): 7415–7428. doi:10.1128/JVI.00080-16. PMC 4984655. PMID 27279608.
- ^ Fehr AR, Perlman S (2015). Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Vol. 1282. pp. 1–23. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1. ISBN 978-1-4939-2437-0. PMC 4369385. PMID 25720466.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ a b "Laboratory testing of human suspected cases of novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection. Interim guidance, 10 January 2020" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 January 2020. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- ^ a b "Novel Coronavirus 2019 (nCoV-2019), Wuhan, China". Archived from the original on 14 January 2020. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 9 January 2020. Retrieved 10 January 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ van der Hoek L, Pyrc K, Jebbink MF, Vermeulen-Oost W, Berkhout RJ, Wolthers KC, Wertheim-van Dillen PM, Kaandorp J, Spaargaren J, Berkhout B (April 2004). "Identification of a new human coronavirus". Nature Medicine. 10 (4): 368–373. doi:10.1038/nm1024. PMID 15034574. Archived from the original on 21 August 2007. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ "WHO Statement Regarding Cluster of Pneumonia Cases in Wuhan, China". www.who.int. 9 January 2020. Archived from the original on 14 January 2020. Retrieved 10 January 2020.
- ^ Doucleef, Michaeleen (26 September 2012). "Scientists Go Deep On Genes Of SARS-Like Virus". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 27 September 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Falco, Miriam (24 September 2012). "New SARS-like virus poses medical mystery". CNN Health. Archived from the original on 1 November 2013. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ "New SARS-like virus found in Middle East". Al-Jazeera. 24 September 2012. Archived from the original on 9 March 2013. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- ^ Kelland, Kate (28 September 2012). "New virus not spreading easily between people: WHO". Reuters. Archived from the original on 24 November 2012. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Nouveau coronavirus – Point de situation : Un nouveau cas d’infection confirmé Archived 8 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine (Novel coronavirus – Status report: A new case of confirmed infection) 12 May 2013 social-sante.gouv.fr
- ^ CDC (2 August 2019). "MERS Transmission". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on 7 December 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ "Novel coronavirus infection - update". World Health Association. 22 May 2013. Archived from the original on 7 June 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ^ CDC (2 August 2019). "MERS in the U.S." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on 15 December 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Sang-Hun, Choe (8 June 2015). "MERS Virus's Path: One Man, Many South Korean Hospitals". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 15 July 2017. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- ^ "Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV)". WHO. Archived from the original on 18 October 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ a b Cruz JL, Sola I, Becares M, Alberca B, Plana J, Enjuanes L, Zuñiga S (June 2011). "Coronavirus gene 7 counteracts host defenses and modulates virus virulence". PLoS Pathogens. 7 (6): e1002090. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002090. PMC 3111541. PMID 21695242.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Cruz JL, Becares M, Sola I, Oliveros JC, Enjuanes L, Zúñiga S (September 2013). "Alphacoronavirus protein 7 modulates host innate immune response". Journal of Virology. 87 (17): 9754–67. doi:10.1128/JVI.01032-13. PMC 3754097. PMID 23824792.
- ^ "the Merck Veterinary Manual". Archived from the original on 9 October 2013. Retrieved 1 June 2013.
- ^ Wertheim JO, Chu DK, Peiris JS, Kosakovsky Pond SL, Poon LL (June 2013). "A case for the ancient origin of coronaviruses". Journal of Virology. 87 (12): 7039–7045. doi:10.1128/JVI.03273-12. PMC 3676139. PMID 23596293.
- ^ Woo PC, Lau SK, Lam CS, Lau CC, Tsang AK, Lau JH, Bai R, Teng JL, Tsang CC, Wang M, Zheng BJ, Chan KH, Yuen KY (April 2012). "Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus". Journal of Virology. 86 (7): 3995–4008. doi:10.1128/JVI.06540-11. PMC 3302495. PMID 22278237.
- ^ Bidokhti MR, Tråvén M, Krishna NK, Munir M, Belák S, Alenius S, Cortey M (September 2013). "Evolutionary dynamics of bovine coronaviruses: natural selection pattern of the spike gene implies adaptive evolution of the strains". The Journal of General Virology. 94 (Pt 9): 2036–2049. doi:10.1099/vir.0.054940-0. PMID 23804565.
- ^ Vijgen L, Keyaerts E, Moës E, Thoelen I, Wollants E, Lemey P, Vandamme AM, Van Ranst M (February 2005). "Complete genomic sequence of human coronavirus OC43: molecular clock analysis suggests a relatively recent zoonotic coronavirus transmission event". Journal of Virology. 79 (3): 1595–1604. doi:10.1128/jvi.79.3.1595-1604.2005. PMC 544107. PMID 15650185.
- ^ Lau SK, Lee P, Tsang AK, Yip CC, Tse H, Lee RA, So LY, Lau YL, Chan KH, Woo PC, Yuen KY (November 2011). "Molecular epidemiology of human coronavirus OC43 reveals evolution of different genotypes over time and recent emergence of a novel genotype due to natural recombination". Journal of Virology. 85 (21): 11325–11337. doi:10.1128/JVI.05512-11. PMC 3194943. PMID 21849456.
- ^ Lau SK, Li KS, Tsang AK, Lam CS, Ahmed S, Chen H, Chan KH, Woo PC, Yuen KY (August 2013). "Genetic characterization of Betacoronavirus lineage C viruses in bats reveals marked sequence divergence in the spike protein of pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5 in Japanese pipistrelle: implications for the origin of the novel Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus". Journal of Virology. 87 (15): 8638–8650. doi:10.1128/JVI.01055-13. PMC 3719811. PMID 23720729.
- ^ Vijaykrishna D, Smith GJ, Zhang JX, Peiris JS, Chen H, Guan Y (April 2007). "Evolutionary insights into the ecology of coronaviruses". Journal of Virology. 81 (8): 4012–4020. doi:10.1128/jvi.02605-06. PMC 1866124. PMID 17267506.
- ^ Gouilh MA, Puechmaille SJ, Gonzalez JP, Teeling E, Kittayapong P, Manuguerra JC (October 2011). "SARS-Coronavirus ancestor's foot-prints in South-East Asian bat colonies and the refuge theory". Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 11 (7): 1690–702. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2011.06.021. PMID 21763784.
- ^ Cui J, Han N, Streicker D, Li G, Tang X, Shi Z, Hu Z, Zhao G, Fontanet A, Guan Y, Wang L, Jones G, Field HE, Daszak P, Zhang S (October 2007). "Evolutionary relationships between bat coronaviruses and their hosts". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 13 (10): 1526–1532. doi:10.3201/eid1310.070448. PMC 2851503. PMID 18258002.
- ^ Crossley BM, Mock RE, Callison SA, Hietala SK (December 2012). "Identification and characterization of a novel alpaca respiratory coronavirus most closely related to the human coronavirus 229E". Viruses. 4 (12): 3689–3700. doi:10.3390/v4123689. PMC 3528286. PMID 23235471.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Huynh J, Li S, Yount B, Smith A, Sturges L, Olsen JC, Nagel J, Johnson JB, Agnihothram S, Gates JE, Frieman MB, Baric RS, Donaldson EF (December 2012). "Evidence supporting a zoonotic origin of human coronavirus strain NL63". Journal of Virology. 86 (23): 12816–12825. doi:10.1128/JVI.00906-12. PMC 3497669. PMID 22993147.
Further reading
- Alwan A, Mahjour J, Memish ZA (2013). "Novel coronavirus infection: time to stay ahead of the curve". Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal. 19 Suppl 1: S3–4. PMID 23888787.
- Laude H, Rasschaert D, Delmas B, Godet M, Gelfi J, Charley B (June 1990). "Molecular biology of transmissible gastroenteritis virus". Veterinary Microbiology. 23 (1–4): 147–54. doi:10.1016/0378-1135(90)90144-K. PMID 2169670.
- Sola I, Alonso S, Zúñiga S, Balasch M, Plana-Durán J, Enjuanes L (April 2003). "Engineering the transmissible gastroenteritis virus genome as an expression vector inducing lactogenic immunity". Journal of Virology. 77 (7): 4357–69. doi:10.1128/JVI.77.7.4357-4369.2003. PMC 150661. PMID 12634392.
- Tajima M (1970). "Morphology of transmissible gastroenteritis virus of pigs. A possible member of coronaviruses. Brief report". Archiv für die Gesamte Virusforschung. 29 (1): 105–8. doi:10.1007/BF01253886. PMID 4195092.
External links
- Virus Pathogen Database and Analysis Resource (ViPR): Coronaviridae
- German Research Foundation (Coronavirus Consortium)
