Portal:Heraldry
Welcome to the Heraldry and Vexillology Portal!


Heraldry encompasses all of the duties of a herald, including the science and art of designing, displaying, describing and recording coats of arms and badges, as well as the formal ceremonies and laws that regulate the use and inheritance of arms. The origins of heraldry lie in the medieval need to distinguish participants in battles or jousts, whose faces were hidden by steel helmets.
Vexillology (from the Latin vexillum, a flag or banner) is the scholarly study of flags, including the creation and development of a body of knowledge about flags of all types, their forms and functions, and of scientific theories and principles based on that knowledge. Flags were originally used to assist military coordination on the battlefield, and have evolved into a general tool for signalling and identification, particularly identification of countries.
Selected biography
Sir Alexander Colin Cole, KCB, KCVO, (16 May 1922–20 February 2001) was a long serving officer of arms at the College of Arms in London. He eventually rose to the rank of Garter Principal King of Arms, the highest heraldic office in England. Prior to his joining the College of Arms he represented the Manchester Palace of Varieties in the Court of Chivalry for the only case it has tried in the last 200 years. He designed the coat of arms for Margaret Thatcher. (more...)
Selected coat of arms

The Royal Coat of Arms of Canada (known formally as the Arms of His/Her Majesty in Right of Canada) is, since 1921, the official coat of arms of the Canadian monarch, and thus also of Canada. It is closely modelled after the royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom with distinctive Canadian elements replacing or added to those derived from the British.
The maple leaves in the shield, blazoned "proper", were originally drawn vert (green) but were redrawn gules (red) in 1957. A circlet of the Order of Canada was added to the arms for limited use in 1987. The shield design forms the Royal Standard of Canada, and the shield is found on the Canadian Red Ensign. The Flag of the Governor General of Canada, which formerly used the shield over the Union Jack, now uses the crest of the arms on a blue field. (more...)
Selected flag

Polish national law defines flags either through an act of parliament or a ministerial ordinance. Apart from the national flag, these are mostly military flags, used by one or all branches of the Polish Armed Forces, especially the Polish Navy. Flags flown by vessels of non-military uniformed services are also included in the list.
Most of the flags feature white and red, the national colors of Poland. The national colors, officially adopted in 1831, are of heraldic origin and derive from the tinctures (colors) of the coats of arms of Poland (the White Eagle) and Lithuania (the Pursuer). Additionally, some flags incorporate the White Eagle itself, either identical with that of the national coat of arms or one of its variants, known as military eagles, used by the Armed Forces. (more...)
Selected picture
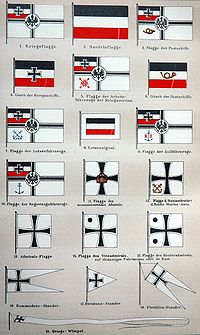
Flags used by the German Kaiserliche Marine (Imperial Navy), 1892.
Did you know...
- ...that several Scottish noble families retain private officers of arms (pictured)?
- ...that British politician Jock Stallard was expelled from the Labour Party in the 1950s for flying the red flag from St Pancras town hall, but later served as a Labour MP and life peer?
- ...that the coat of arms of Greenland depicts a polar bear raising its left forepaw, breaking with the heraldic tradition of showing the right forepaw raised, because polar bears are left-handed?
- ...that the current flag of Bhutan was introduced after it was noticed the previous square version didn't flutter like the flag of India?
- ...that President Lyndon Johnson was granted a coat of arms by the American College of Heraldry and Arms in 1968?
Related portals
|
|
|
Heraldry Web resources
Authorities
- Belgium - The Council of Nobility, Flemish Heraldic Council and Council of Heraldry and Vexillology of the French Community
- Canada - Canadian Heraldic Authority and see also Public Register of Arms, Flags and Badges
- England, Wales, and Northern Ireland - The College of Arms
- Ireland - The Office of the Chief Herald of Ireland
- Netherlands - High Council of Nobility
- Portugal - Instituto da Nobreza Portuguesa
- Scotland - The Court of the Lord Lyon
- South Africa - South African Bureau of Heraldry
- Sweden - National Board of Heraldry, The National Archive
- United States Army - The United States Army Institute of Heraldry
Societies
- Greek Heraldry Society
- The Academy of Heraldic Science Czech republic
- The American College of Heraldry
- The American Heraldry Society
- The Augustan Society
- The Australian Heraldry Society Inc.
- Bulgarian Heraldry and Vexillology Society
- The Center for Research of Orthodox Monarchism
- Cambridge University Heraldic and Genealogical Society
- Chiltern Heraldry Group
- The College of Dracology
- Croatian Heraldic and Vexillologic Association
- The Finnish Heraldic Society
- Fryske Rie foar Heraldyk
- Hellenic Armigers Society
- Guild of Heraldic Artists
- Genealogical Society of Ireland
- Heraldry Research Institute (Japan)
- The Heraldry Society
- The Heraldry Society of Africa
- The Heraldry Society of New Zealand Inc.
- The Heraldry Society of Scotland
- The Heraldry Society of Southern Africa
- The Institute of Heraldic and Genealogical Studies
- The International Association of Amateur Heralds
- Italian Center of Vexillological Studies
- Lancashire Heraldry Group
- Macedonian Heraldry Society
- New England Historic Genealogical Society Committee on Heraldry
- Norwegian Heraldry Society
- Oxford University Heraldry Society
- Polish Heraldry Society
- Polish Nobility Confederation
- Real Academia Matritense de Heráldica y Genealogía - Royal Academy of Heraldry and Genealogy of Madrid
- Romanian Institute for Genealogy and Heraldry
- The Royal Heraldry Society of Canada
- The Russian College of HeraldryThe Russian College of Heraldry
- Serbian Heraldic Society
- Societas Heraldica Scandinavica
- Societas Heraldica Slovenica
- Swedish Heraldic Society
- Ukrainian Heraldry Society
- Royal Association Genealogical and Heraldic Office of Belgium
Vexillology
Software
- Coat of Arms Visual Designer web-based program
- Puncher Heraldry Program
- Blazonry Server - pyBlazon
- DrawShield - creates SVG shield or arms image from blazon
- CoaMaker - web-based tool
- Blazon95 and BLAZONS! 2000, older Windows applications
Texts
- Heraldry, historical and popular : with seven hundred illustrations (1863)
- A Complete Guide to Heraldry (1909)
Other
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus












