Languages of Scotland
| Languages of Scotland | |
|---|---|
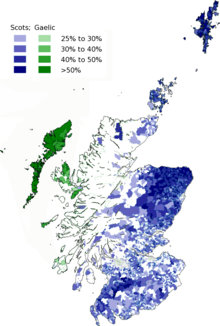 Geographic distribution of Scots and Scottish Gaelic speakers in Scotland | |
| Official | Scottish English, Scots, Scottish Gaelic and British Sign Language[1] |
| Main | Scottish English (98.6%)[2] |
| Minority | Scots (30.1%), Scottish Gaelic (1.1%)[2] |
| Foreign | Polish (1.1%), Urdu (0.5%), Chinese (0.5%), Punjabi (0.5%)[3] |
| Signed | British Sign Language (official) |
| Keyboard layout | |
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Scotland |
|---|
 |
| People |
| Mythology and folklore |
| Cuisine |
| Religion |
| Art |
| Literature |
The languages of Scotland belong predominantly to the Germanic and Celtic language families. The main language now spoken in Scotland is English, while Scots and Scottish Gaelic are minority languages. The dialect of English spoken in Scotland is referred to as Scottish English.
Celtic languages
[edit]The Celtic languages of Scotland can be divided into two groups: Goidelic (or Gaelic) and Brittonic (or Brythonic). Pictish is usually seen as a Brittonic language but this is not universally accepted. They are known collectively as the Insular Celtic languages.
Goidelic languages
[edit]
The Goidelic language currently spoken in Scotland is Scottish Gaelic. It is widely spoken in the Outer Hebrides, and also in parts of the Inner Hebrides and Scottish Highlands, and by some people in other areas of Scotland. It was formerly spoken over a far wider area than today, even in the recent past, as evidenced by placenames. Galwegian Gaelic is the extinct dialect of Scottish Gaelic formerly spoken in southwest Scotland. It was spoken by the independent kings of Galloway in their time, and by the people of Galloway and Carrick until the early modern period. It was also once spoken, but much less so in Annandale and Strathnith.
Scottish Gaelic, along with modern Manx and Irish, is descended from Middle Irish, a derivative of Old Irish, which is descended in turn from Primitive Irish, the oldest known form of the Goidelic languages. Primitive Irish is known only from fragments, mostly personal names, inscribed on stone in the Ogham alphabet in Ireland and western Britain up to about the 6th century AD.
Goidelic languages were once the most prominent by far among the Scottish population, but are now mainly restricted to the West. The Beurla-reagaird is a Gaelic-based cant of the Scottish travelling community related to the Shelta of Ireland.[4]
The majority of the vocabulary of modern Scottish Gaelic is native Celtic. There are a large number of borrowings from Latin, (muinntir, Didòmhnaich), ancient Greek, especially in the religious domain (eaglais, Bìoball from ἐκκλησία ekklesia and βίβλος biblos), Norse (eilean, sgeir), Hebrew (Sàbaid, Aba), French (seòmar) and Scots (aidh, bramar).

In common with other Indo-European languages, the neologisms which are coined for modern concepts are typically based on Greek or Latin, although written in Gaelic orthography; "television", for instance, becomes telebhisean and "computer" becomes coimpiùtar. Although native speakers frequently use an English word for which there is a perfectly good Gaelic equivalent, they will, without thinking, simply adopt the English word and use it, applying the rules of Gaelic grammar, as the situation requires. With verbs, for instance, they will simply add the verbal suffix (-eadh, or, in Lewis, -igeadh, as in, "Tha mi a' watcheadh (Lewis, "watchigeadh") an telly" (I am watching the television), rather than "Tha mi a' coimhead air an telebhisean". This tendency was remarked upon by the minister who compiled the account covering the parish of Stornoway in the New Statistical Account of Scotland, published over 170 years ago. It has even gone so far as the verb Backdatigeadh. However, as Gaelic medium education grows in popularity, a newer generation of literate Gaels is becoming more familiar with modern Gaelic vocabulary.
The influence of Scottish Gaelic can be seen particularly in surnames (notably Mac- names, where the mac means "Son of...") and toponymy. The surname influence is not restricted to Mac- names: several colours give rise to common Scottish surnames: bàn (Bain – white), ruadh (Roy – red), dubh (Dow – black), donn (Dunn – brown), buidhe (Bowie – yellow), and Gille- (meaning lad or servant) gives rise to names such as Gilmour and Gillies. Common place name elements from Gaelic in Scotland include baile (Bal-, a town) e.g. Balerno, cille (Kil-, an old church) e.g. Kilmarnock, inbhir (Inver-, Inner-, meaning a confluence) e.g. Inverness, Innerleithen, ceann (Kin-, meaning a head or top of something) e.g. Kintyre, Kinross, and dun (meaning a fort) e.g. Dundee and Dunfermline.
Brittonic languages
[edit]
None of the Brittonic languages of Scotland survive to the modern day, though they have been reconstructed to a degree.
The ancestral Common Brittonic language was probably spoken in southern Scotland in Roman times and earlier.[5] It was certainly spoken there by the early medieval era, and Brittonic-speaking kingdoms such as Strathclyde, Rheged, and Gododdin, part of the Hen Ogledd ("Old North"), emerged in what is now Scotland. Eventually Brittonic evolved into a variety known as Cumbric, which survived in southwestern Scotland until around the 11th century.
The main legacy of these languages has been Scotland's toponymy, e.g. names such as Aberdeen, Tranent and Ochiltree.
There are also many Brittonic influences on Scottish Gaelic. Scottish Gaelic contains a number of apparently P-Celtic loanwords, but as Q-Celtic has a far greater overlap with P-Celtic than with English in terms of vocabulary, it is not always possible to disentangle P- and Q-Celtic words. However some common words, such as monadh ≡ Welsh mynydd, Cumbric *monidh, are particularly evident. Often the Brittonic influence on Scots Gaelic is indicated by comparing with the Irish Gaelic usage which is not likely to have been influenced so much by Brittonic. In particular, the word srath (anglicised as "Strath") is a native Goidelic word, but its usage appears to have been modified by its Brittonic cognate ystrad, whose meaning is slightly different.
Pictish language
[edit]The Pictish language is an Insular Celtic language. At its height, it may have been spoken from Shetland down to Fife, but it was pushed back as Scots and Anglo-Saxons invaded Northern Britain, each with their own language. Pritennic may have been a precursor of Pictish.[6]
Germanic languages
[edit]Two West Germanic languages in the Anglic group are spoken in Scotland today: Scots, and Scottish English, a dialect of the English language. The Norn language, a North Germanic language, is now extinct.
The Northumbrian Old English dialect of the Old English was spoken in the Anglian Kingdom of Northumbria from the Humber estuary to the Firth of Forth. The Viking invasions of the 9th century forced the dialect to split in two and in the north it began to evolve into Scots.[citation needed]
Scots language
[edit]
Scots has its origins in the variety of early northern Middle English spoken in southeastern Scotland, also known as Early Scots. That began to diverge from the Northumbrian variety due to 12th and 13th century immigration of Scandinavian-influenced Middle English-speakers from the North and Midlands of England.[7]: xliii Later influences on the development of Scots were from Romance languages via ecclesiastical and legal Latin, Norman[7]: lxiii–lxv and later Parisian French due to the Auld Alliance; as well as Dutch and Middle Low German influences due to trade and immigration from the Low Countries.[7]: xliii Scots also includes loan words resulting from contact with Scottish Gaelic. Early medieval legal documents include a body of Middle Gaelic legal and administrative loanwords.[7]: lxi Contemporary Scottish Gaelic loanwords are mainly for geographical and cultural features, such as ceilidh, loch and clan, and also occur in colloquialisms such as gob and jilt.
From the 13th century Early Scots spread further into Scotland via the burghs, early urban institutions which were first established by King David I. The growth in prestige of Early Scots in the 14th century, and the complementary decline of French in Scotland, made Scots the prestige language of most of eastern Scotland. By the 16th century Middle Scots had established orthographic and literary norms largely independent of those developing in England.[8] "Modern Scots" is used to describe the language after 1700, when southern Modern English was generally adopted as the literary language.
There is no institutionalised standard variety, but during the 18th century a new literary language descended from the old court Scots emerged. This variety abandoned some of the more distinctive old Scots spellings,[9] adopted many standard English spellings (although from the rhymes it is clear that a Scots pronunciation was intended)[10]: xv and introduced what came to be known as the apologetic apostrophe,[10]: xiv generally occurring where a consonant exists in the Standard English cognate. This Written Scots drew not only on the vernacular but also on the King James Bible, and was also heavily influenced by the norms and conventions of Augustan English poetry.[11] Consequently, this written Scots looked very similar to contemporary Standard English, suggesting a somewhat modified version of that, rather than a distinct speech form with a phonological system which had been developing independently for many centuries.[12] This modern literary dialect, "Scots of the book" or Standard Scots[13] once again gave Scots an orthography of its own, lacking neither "authority nor author".[14] During the 20th century a number of proposals for spelling reform were presented. Commenting on this, John Corbett (2003: 260) writes that "devising a normative orthography for Scots has been one of the greatest linguistic hobbies of the past century". Most proposals entailed regularising the use of established 18th and 19th century conventions, in particular the avoidance of the apologetic apostrophe.
Spoken Scots comprises many dialects, none of which may be said to be more "true" Scots than any other. This diversity is often seen as a mark of local pride among Scots. There are four dialect groupings: Insular Scots, spoken in Orkney and Shetland; Northern Scots, spoken in Caithness, Easter Ross, Moray, Aberdeenshire, and Angus; Central Scots, spoken in the Central Lowlands and South West Scotland; and Southern Scots, spoken in the Scottish Borders and Dumfriesshire. A Jewish hybrid of the early 20th century is Scots-Yiddish.
Scottish English
[edit]
Scottish (Standard) English is the result of language contact between Scots and the Standard English of England after the 17th century. The resulting shift towards Standard English by Scots-speakers resulted in many phonological compromises and lexical transfers, often mistaken for mergers by linguists unfamiliar with the history of Scottish English.[15]: 60–61 Furthermore, the process was also influenced by interdialectal forms, hypercorrections and spelling pronunciations.[15]: 61 Highland English has been influenced by Gaelic. The most Gaelic influenced variety being Hebridean English, spoken in the Western Isles.
Distinct vocabulary, often from Latin and Lowland Scots, is still used in Scottish legal terminology.
Norn language
[edit]Norn is an extinct North Germanic, West Scandinavian, language that was spoken in Shetland and Orkney, off the north coast of mainland Scotland, and in Caithness. Norn evolved from the Old Norse that was widely spoken in the Hebrides, Orkney, Shetland and the west coast of the mainland during the Viking occupation from the 8th to the 13th centuries. After the Northern Isles were ceded to Scotland by Norway in the 15th century, its use was discouraged by the Scottish government and the Church of Scotland (the national church), and it was gradually replaced by Lowland Scots over time. Norn persisted well into the 19th century, as the Faroese linguist Jakob Jakobsen wrote:
As late as 1894, there were people in Foula who could repeat sentences in Norn, as I myself had the opportunity of hearing. The last man in Unst who is said to have been able to speak Norn, Walter Sutherland from Skaw, died about 1850. In Foula, on the other hand, men who were living very much later than the middle of the present [19th] century are said to have been able to speak Norn[16]
Most of the use of Norn/Norse in modern-day Shetland and Orkney is purely ceremonial, and mostly in Old Norse, for example the Shetland motto, which is Með lögum skal land byggja ("with law shall land be built"), which is the same motto used by the Icelandic police force and inspired by the Danish Codex Holmiensis.
There are some enthusiasts who are engaged in developing and disseminating a modern form called Nynorn ("New Norn"), based upon linguistic analysis of the known records and Norse linguistics in general.[17][18]
Norman French, Ancient Greek and Latin
[edit]
Latin is also used to a limited degree in certain official mottos, for example Nemo Me Impune Lacessit, legal terminology (Ultimus haeres and condictio causa data causa non-secuta), and various ceremonial contexts. Latin abbreviations can also be seen on British coins and in mottos etc. The use of Latin has declined greatly in recent years. At one time, Latin and Ancient Greek were commonly taught in Scottish schools (and were required for entrance to the ancient universities until 1919, for Greek, and the 1960s, for Latin[19]), and Scottish Highers are still available in both subjects. Latin's presence is almost two thousand years old in Scotland, but it has rarely been a community language.
Norman French was historically used in Scotland, and appears in some mottos as well. Some works of medieval literature from Scotland were composed in this language. After the twelfth-century reign of King David I and the so-called "Davidian Revolution", the Scottish monarchs are perhaps better described as Scoto-Norman than Gaelic, often preferring French culture to native Scottish culture. A consequence was the spread of French institutions and social values including Canon law. The first towns, called burghs, appeared in the same era, and as they spread, so did the Middle English language. These developments were offset by the acquisition of the Norse-Gaelic west, and the Gaelicisation of many of the noble families of French and Anglo-French origin and national cohesion was fostered with the creation of various unique religious and cultural practices. By the end of the period, Scotland experienced a "Gaelic revival" which created an integrated Scottish national identity.
The use of Ancient Greek is almost entirely gone in Scotland, but one example would be the motto of St Andrews University, ΑΙΕΝ ΑΡΙΣΤΕΥΕΙΝ (AIEN ARISTEUEIN) ("Ever to Excel" or "Ever To Be The Best")[20]
Sign languages
[edit]
Scotland's deaf community tends to use British Sign Language. There are a few signs used in Scotland which are unique to the country, as well as variations in some signs from Dundee to Glasgow (similar to accents). Most deaf people in Scotland are educated in mainstream schools.
Other sign languages in use in Scotland include Makaton, and Signed English, a sign language based on the English language.
Controversies
[edit]Language vs dialect
[edit]There are no universally accepted criteria for distinguishing languages from dialects, although a number of paradigms exist, which render sometimes contradictory results. The exact distinction is therefore a subjective one, dependent on the user's frame of reference. (See Dialect)
Scottish Gaelic and Irish are generally viewed as being languages in their own right rather than dialects of a single tongue but are sometimes mutually intelligible to a limited degree – especially between southern dialects of Scottish Gaelic and northern dialects of Irish (programmes in each form of Gaelic are broadcast on BBC Radio nan Gaidheal and RTÉ Raidió na Gaeltachta), but the relationship of Scots and English is less clear, since there is usually partial mutual intelligibility.
Since there is a very high level of mutual intelligibility between contemporary speakers of Scots in Scotland and in Ulster (Ulster Scots dialect), and a common written form was current well into the 20th century, the two varieties have usually been considered as dialects of a single tongue rather than languages in their own right; the written forms have diverged in the 21st century. The government of the United Kingdom "recognises that Scots and Ulster Scots meet the Charter's definition of a regional or minority language".[21] Whether this implies recognition of one regional or minority language or two is a question of interpretation. Ulster Scots is defined in legislation (The North/South Co-operation (Implementation Bodies) Northern Ireland Order 1999) as: the variety of the Scots language which has traditionally been used in parts of Northern Ireland and in Donegal in Ireland.[22]
Hostility
[edit]Some resent Scottish Gaelic being promoted in the Lowlands, although it was once spoken everywhere in mainland Scotland including, to an extent, the extreme south-east[23][24] (that part of Scotland which was originally Northumbria) and the extreme north-east (Caithness).
Two areas with mostly Norse-derived placenames (and some Pictish), the Northern Isles (Shetland and Orkney) were ceded to Scotland in lieu of an unpaid dowry in 1472, and never spoke Gaelic; its traditional vernacular Norn, a derivative of Old Norse mutually intelligible with Icelandic and Faroese, died out in the 18th century after large-scale immigration by Lowland Scots speakers. To this day, many Shetlanders and Orcadians maintain a separate identity, albeit through the Shetland and Orcadian dialects of Lowland Scots, rather than their former national tongue. Norn was also spoken at one point in Caithness, apparently dying out much earlier than Shetland and Orkney. However, the Norse speaking population were entirely assimilated by the Gaelic speaking population in the Western Isles; to what degree this happened in Caithness is a matter of controversy, although Scottish Gaelic was spoken in parts of the county until the 20th century.
Overview
[edit]Diagrammatic representation of the development of the historic Indo-European languages of Scotland:
Statistics
[edit]According to the 2001 census Scottish Gaelic has 58,652 speakers (roughly 1% of the population of Scotland). In total 92,400 people aged three and over in Scotland had some Gaelic language ability in 2001.[25] 15,723 of these reside in the Outer Hebrides, where the language is spoken by the majority of the population.[26] There are also large populations of speakers in other parts of the Highlands.
In a 2010 Scottish Government study, 85% of respondents noted they speak Scots.[27] According to the 2011 census, 1,541,693 people can speak Scots in Scotland, approximately 30% of the population.[2]
The 2011 census asked people to specify the language that they used at home.[28] This found that the language used by majority of people aged 3 and over (92.6%) was English.[3]
| Mother tongue | Count of all people aged 3 or over | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| English | 4,740,547 | 94.5% |
| Scots | 55,817 | 1.1% |
| Polish | 54,186 | 1.1% |
| Chinese (Cantonese, Mandarin, Min Nan, etc.) |
27,381 | 0.6% |
| Gaelic (Scottish and others) | 24,974 | 0.5% |
| Urdu | 23,394 | 0.5% |
| Punjabi | 23,150 | 0.5% |
| French | 14,623 | 0.3% |
| British Sign Language | 12,533 | 0.3% |
| German | 11,317 | 0.2% |
Other
[edit]- The Romani language (Indo-Aryan) has also been spoken in Scotland, but became more or less extinct in the country during the 20th century. It has lent Scotland's other languages a number of loanwords, and has also had an effect on the Gaelic of the travelling community. Since the beginning of the 21st century increasing numbers of Romani migrants from Eastern Europe has seen the Romani language return to Scotland. The Govanhill area in Glasgow has become home to many Romani people and the Romani language can be heard being spoken in the area.
- Beurla Reagaird, a Scottish analogy to Shelta, being a form of Gaelic or semi-Gaelicised English spoken by some travellers.
- During the 20th and 21st centuries immigrants from a wide variety of countries have created a complex mosaic of spoken languages amongst the resident population.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Languages". www.gov.scot. Retrieved 11 October 2024.
- ^ a b c United Kingdom census (2011). "Table KS206SC - Language" (PDF). National Records of Scotland. Retrieved 13 April 2021.
- ^ a b c United Kingdom census (2011). "Table AT_002_2011 - Language used at home other than English (detailed), Scotland". National Records of Scotland. Retrieved 13 April 2021.
- ^ Neat, Timothy (2002) The Summer Walkers. Edinburgh. Birlinn. pp.225–29.
- ^ Jackson, Kenneth Hurlstone (1953). Language and History in Early Britain. University Press.
- ^ Jackson K; The Pictish Language in F T Wainright "The Problem of the Picts" (1955).
- ^ a b c d Macafee, Caroline; Aitken, A. J. (2002). "A history of Scots to 1700". A Dictionary of the Older Scottish Tongue. Vol. 12.
- ^ Corbett, John; McClure, Derrick; Stuart-Smith, Jane, eds. (2003). "A Brief History of Scots". The Edinburgh Companion to Scots. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. pp. 9ff. ISBN 0-7486-1596-2.
- ^ Tulloch, Graham (1980). The Language of Walter Scott: A Study of his Scottish and Period Language. London: Deutsch. p. 249.
- ^ a b Grant and, William; Murison, David D., eds. (1929–1976). Scottish National Dictionary. Vol. I. Edinburgh: The Scottish National Dictionary Association.
- ^ McClure, J. D. (1992). The Oxford Companion to the English Language. Oxford University Press. p. 168.
- ^ J. Derrick, McClure (1985). "The debate on Scots orthography". In Görlach, Manfred (ed.). Focus on: Scotland. Amsterdam: Benjamins. p. 204.
- ^ Mackie, Albert D. (1952). "Fergusson's Language: Braid Scots Then and Now". In Smith, Syndney Goodsir (ed.). Robert Fergusson 1750–1774. Edinburgh: Nelson. pp. 123–124, 129.
- ^ Stevenson, R. L. (1905). "Underwoods". The Works of R. L. Stevenson. Vol. 8. London: Heinemann. p. 152.
- ^ a b Macafee, C. (2004). Hikey, R. (ed.). Legacies of Colonial English: Studies in Transported Dialects. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Barnes, Michael (2010). Millar, Robert McColl (ed.). "The Study of Norn" (PDF). Northern Lights, Northern Words. Selected Papers from the FRLSU Conference, Kirkwall 2009. Aberdeen: Forum for Research on the Languages of Scotland and Ireland: 40. ISBN 978-0-9566549-1-5.
- ^ "Norn". Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- ^ "Welcome". Shetlopedia.
- ^ Bryn Mawr Classical Review 98.6.16. Ccat.sas.upenn.edu. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "University Coat of Arms; University of St Andrews". Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- ^ List of declarations made with respect to treaty No. 148, European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, Status as of: 17 March 2011
- ^ European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (archived from the original on 14 May 2005), Council of Europe.
- ^ Robinson, Mairi, ed. (1985). The Concise Scots Dictionary (1987 ed.). Aberdeen: Aberdeen University Press. p. ix. ISBN 0080284914.
by the tenth and eleventh centuries the Gaelic language was in use throughout the whole of Scotland, including the English-speaking south-east, though no doubt the longer-established Northern English continued to be the dominant language there
- ^ Aitken, A. (1985). "A history of Scots" (PDF). media.scotslanguage.com.
- ^ "News Release – Scotland's Census 2001 – Gaelic Report" Archived 22 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine from General Registrar for Scotland website, 10 October 2005. Retrieved 27 December 2007
- ^ "Census 2001 Scotland: Gaelic speakers by council area" Comunn na Gàidhlig. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
- ^ The Scottish Government. "Public Attitudes Towards the Scots Language". Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- ^ "Language used at home".
Further reading
[edit]- Lauchlan, Fraser; Parisi, Marinella; Fadda, Roberta (2013). "Bilingualism in Sardinia and Scotland: Exploring the cognitive benefits of speaking a 'minority' language". International Journal of Bilingualism. 17 (1): 43–56. doi:10.1177/1367006911429622. S2CID 145120231. - Available at Gale Academic Onefile

