Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests
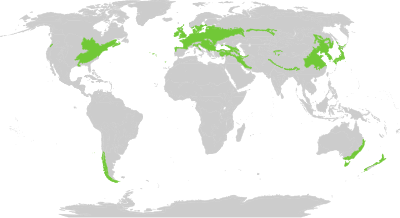

Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial biome, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions.
The term 'Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest' is used by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) in global biogeography as one of the biome designations under which to organize ecoregions.[1]
Ecology
The typical structure of these forests includes four layers. The uppermost layer is the canopy composed of tall mature trees ranging from 30 to 61 m (100 to 200 ft) high. Below the canopy is the three-layered, shade-tolerant understory that is roughly 9 to 15 m (30 to 50 ft) shorter than the canopy. The top layer of the understory is the sub-canopy composed of smaller mature trees, saplings, and suppressed juvenile canopy layer trees awaiting an opening in the canopy. Below the sub-canopy is the shrub layer, composed of low growing woody plants. Typically the lowest growing (and most diverse) layer is the ground cover or herbaceous layer.
Trees
In the Northern hemisphere, characteristic dominant broadleaf trees in this biome include oaks (Quercus spp.), beeches (Fagus spp.), maples (Acer spp.), or birches (Betula spp.).[2] The term "mixed forest" comes from the inclusion of coniferous trees as a canopy component of some of these forests. Typical coniferous trees include: Pines (Pinus spp.), firs (Abies spp.), and spruces (Picea spp.). In some areas of this biome the conifers may be a more important canopy species than the broadleaf species. In the Southern hemisphere, endemic genera such as Nothofagus and Eucalyptus occupy this biome.
Climate
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests occur in areas with distinct warm and cool season, which give it a moderate annual average temperature — 3 to 15.6 °C (37 to 60 °F). These forests occur in relatively warm and rainy climates, sometimes also with a distinct dry season. A dry season occurs in the winter in East Asia and in summer on the wet fringe of the Mediterranean climate zones. Other areas, as in the central and upper eastern United States and southeastern Canada, have a fairly even distribution of rainfall; annual rainfall is typically over 600 mm (24 in) and often over 1,500 mm (59 in). Temperatures are typically moderate except in parts of Asia such as Ussuriland where temperate forests can occur despite very harsh conditions with very cold winters.
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest ecoregions
Australasia
| Chatham Islands temperate forests | New Zealand |
| Eastern Australian temperate forests | Australia |
| Fiordland temperate forests | New Zealand |
| Nelson Coast temperate forests | New Zealand |
| North Island temperate forests | New Zealand |
| Northland temperate kauri forests | New Zealand |
| Stewart Island / Rakiura temperate forests | New Zealand |
| Richmond temperate forests | New Zealand |
| Southeast Australia temperate forests | Australia |
| Southland temperate forests | New Zealand |
| Tasmanian Central Highland forests | Australia |
| Tasmanian temperate forests | Australia |
| Tasmanian temperate rain forests | Australia |
| Westland temperate forests | New Zealand |
Eurasia
Americas
| Juan Fernandez Islands temperate forests | Chile |
| Magellanic subpolar forests | Argentina, Chile |
| San Félix–San Ambrosio Islands temperate forests | Chile |
| Valdivian temperate forests | Argentina, Chile |
See also
- Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests topics
- Forest topics
- Kuchler plant association system
- Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub
- Temperate deciduous forest
- Trees of the world
