Tropical Storm Dorothy
 Satellite image of the storm east of the Lesser Antilles | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | August 17, 1970 |
| Dissipated | August 23, 1970 |
| Tropical storm | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Highest winds | 70 mph (110 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 996 mbar (hPa); 29.41 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | Up to 51 direct |
| Damage | $34 million (1970 USD) |
| Areas affected | Lesser Antilles (Martinique landfall) |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 1970 Atlantic hurricane season | |
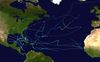
Tropical Storm Dorothy was the deadliest tropical cyclone of the 1970 Atlantic hurricane season. The fourth named storm and fifth tropical storm or hurricane of the season, Dorothy developed on August 17 from a tropical wave to the east of the Lesser Antilles. It tracked west-northwestward throughout its entire duration, and despite forecasts of attaining hurricane status, Dorothy reached peak winds of 70 mph (110 km/) – slightly below hurricane status. The storm struck Martinique on August 20, and subsequently began a gradual weakening trend in the Caribbean Sea. On August 23, Dorothy dissipated south of Hispaniola.
Most significantly affected by the storm was Martinique, which received 26.8 in (680 mm) of rainfall in a 24‑hour period. The rainfall caused flooding and mudslides, resulting in about $34 million in damage (1970 USD); 186 homes were destroyed, and 700 people were left homeless. The flooding killed up to 50 people on the island. Elsewhere in the Lesser Antilles, the storm killed one person on Dominica from heavy rainfall, and in Guadeloupe heavy damage to the banana crop was reported.
Meteorological history
[edit]
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
The origins of Tropical Storm Dorothy were from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa on August 13.[1] It tracked generally westward, developing into a tropical depression on August 17 about 1,375 miles (2,215 km) east of Tobago in the Lesser Antilles.[2] Two days later, it strengthened into Tropical Storm Dorothy, while located about 500 mi (800 km) east of the Lesser Antilles, with its intensity confirmed by the hurricane hunters.[1]
With light vertical wind shear and warm water temperatures, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) remarked on August 19 that "hurricane status would probably be attained this afternoon or tonight." Its track was expected to continue generally west-northwestward, influenced by a ridge near the Bahamas, and within 60 hours Dorothy was forecast to be north or over Puerto Rico.[3] However, a subsequent hurricane hunters flight reported a more westerly motion, which would bring its track through the central Lesser Antilles.[4] Tropical Storm Dorothy gradually intensified, reaching peak winds of 70 mph (110 km/h) on August 20 just east-northeast of Barbados.[2] hurricane hunters confirmed the intensity, though the flight also reported a weakness of low-level inflow.[5] Despite maintaining winds of just below hurricane-force, there was no evidence of an eyewall on radars as the storm approached the Lesser Antilles.[6] Late on August 20, the storm moved across Martinique into the Caribbean Sea, during which its low-level circulation became disorganized.[7]
As Tropical Storm Dorothy moved further into the Caribbean Sea, it began a gradual weakening trend initiated by a persistent tropical upper tropospheric trough,[1] as well as the presence of strong wind shear and a lack of inflow.[8] Hurricane Hunter flights late on August 21 and early on August 22 failed to locate a closed low-level circulation, and as a result the storm was downgraded to a tropical depression.[9] After another flight into the system could not detect a circulation, the NHC discontinued advisories on Dorothy to the south of Hispaniola late on August 22. Around the same time, thunderstorms increased in association with the cyclone, and forecasters remarked the potential for re-intensification over the western Caribbean Sea.[10] However, the storm became more disorganized, and on August 23 Dorothy degenerated into a tropical wave.[1]
Preparations and impact
[edit]| Precipitation | Storm | Location | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | mm | in | |||
| 1 | 680.7 | 26.80 | Dorothy 1970 | Fourniols | [11] |
| 2 | 567.0 | 22.32 | Klaus 1990 | Le Morne-Rouge | [12] |
| 3 | 475.0 | 18.07 | Beulah 1967 | Les Anses-d'Arlets | [13] |
| 4 | 450.1 | 17.72 | Iris 1995 | Ducos | [14] |
| 5 | 349.0 | 13.74 | David 1979 | Saint-Joseph | [15] |
| 6 | 332.0 | 13.07 | Dean 2007 | Fort-de-France | [16] |
| 7 | 305.0 | 12.01 | Cindy 1993 | Le Prêcheur | [17] |
| 8 | 301.5 | 11.87 | Edith 1963 | Saint-Pierre | [18] |
| 9 | 280.0 | 11.02 | Allen 1980 | Grand-Rivière | [19] |
| 10 | 230.1 | 9.059 | Marilyn 1995 | Le Morne-Rouge | [20] |
After the first tropical cyclone advisory was issued on Tropical Storm Dorothy, a hurricane watch and storm warning were issued for the Leeward Islands from Dominica northward.[21] As its westward track became more apparent, the watches and warnings were extended southward to include Martinique and Saint Lucia.[4] On Martinique, authorities released a statement that warned the public for the potential for strong winds, heavy rainfall, and rough waves.[22] Also on the island, officials converted schools and government buildings into shelters for people in low-lying areas.[23] As a result of the storm, the Martinique Aimé Césaire International Airport in Le Lamentin was closed.[24]
The storm dropped heavy rainfall while crossing the Lesser Antilles. In Martinique, the highest 24-hour total was 26.8 inches (680 mm) in Fourniols, which was twice the average rainfall for August. Additionally, the capital city of Fort-de-France reported 13.4 in (341 mm).[25] There, the rainfall broke all records for durations up to 24 hours; about 1 inch (25 mm) fell in 5 minutes, and in one hour a station reported 6.02 inches (153 mm).[26] The rainfall caused flooding and mudslides,[1] as well as rivers exceeding their banks;[27] several bridges collapsed during the storm, and many homes were washed away.[24] During the passage of the storm, sustained winds on the island reached 67 miles per hour (108 km/h), with gusts reaching 99 miles per hour (159 km/h) in the Caravelle peninsula.[28] Throughout the country, the storm destroyed 186 homes and left 700 people homeless.[27] The passage of Dorothy left heavy crop damage on the island, totaling 32 million francs (1970 FRF, $5.8 million 1970 USD); a total of 3.75 sq mi (9.7 km2) of banana crop was destroyed, and 2.16 sq mi (5.6 km2) of sugar cane was destroyed. Damage on the island totaled 190 million francs (1970 FRF, $34 million 1970 USD).[27]
Tropical Storm Dorothy caused several deaths on Martinique, although the exact death toll is unknown. The National Hurricane Center reported 50 deaths,[1] although the post event report provided by the French meteorological agency reported 44 people dead or missing.[27] Most of the deaths were in Saint-Joseph, where 20 people drowned in the Rivière l'Or.[27] Floodwater rescues had been made difficult due to washed out roads and poor communications after the storm.[29] In addition to the deaths, several people were injured.[27] After the passage of the storm, Martinique was temporarily left isolated, when communications were downed with other nearby islands.[24] The French Red Cross distributed 500 blankets and one ton of condensed milk; the agency also sought international assistance.[29]
Elsewhere in the Lesser Antilles, the storm caused flooding and mudslides in Dominica.[1] There, the storm caused one death, when flooding heavy rainfall washed out a bridge. Also, all of the capital city of Roseau lost power and water service due to the storm.[24] In neighboring Guadeloupe, the storm left much of the banana crop destroyed.[29] Later, after it entered the Caribbean Sea, small craft warnings were issued for the Leeward Islands, the Virgin Islands, and Puerto Rico.[7] In its review of the storm, the National Hurricane Center did not mention any damage in the Greater Antilles.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h National Hurricane Center (1970). "Tropical Storm Dorothy Preliminary Report (Page 1)". Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ a b "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. April 5, 2023. Retrieved January 1, 2025.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Landsea, Chris (April 2022). "The revised Atlantic hurricane database (HURDAT2) - Chris Landsea – April 2022" (PDF). Hurricane Research Division – NOAA/AOML. Miami: Hurricane Research Division – via Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory.
- ^ Frank (August 19, 1970). "Tropical Storm Dorothy Discussion". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ a b Hebert (August 19, 1970). "Tropical Storm Dorothy Discussion". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ Kraft (August 20, 1970). "Tropical Storm Dorothy Discussion". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ Frank (August 20, 1970). "Tropical Storm Dorothy Discussion". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ a b Hope (August 21, 1970). "Tropical Storm Dorothy Discussion". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ Frank (August 21, 1970). "Tropical Storm Dorothy Discussion". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ Frank (August 22, 1970). "Tropical Storm Dorothy Discussion". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ Hope (August 22, 1970). "Tropical Depression Dorothy Discussion". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ Perrusset, Marcell; Bouguen, Pierre (1970). La Tempête Tropicale Dorothy (Report) (in French). Météo-France. table 1 as archived by the National Hurricane Center in its Storm Wallet for Tropical Storm Dorothy, 1970. Retrieved January 24, 2012.
- ^ 1990 Klaus: Ouragan. Pluies extrêmes aux Antilles (Report) (in French). Météo-France. n.d. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ 1967 Beulah: Ouragan. Pluies extrêmes aux Antilles (Report) (in French). Météo-France. n.d. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ Rappaport, Edward N. (November 2, 2000). "Hurricane Iris: 22 August–4 September 1995" (PDF). 1995 Atlantic Hurricane Season (Preliminary Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ 1979 David: Ouragan. Pluies extrêmes aux Antilles (Report) (in French). Météo-France. n.d. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ Franklin, James L (January 31, 2008). Hurricane Dean (AL042007): August 13–23 2007 (PDF) (Technical report). National Hurricane Center. p. 4. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ Mayfield, Britt M (October 25, 1993). "Tropical Storm Cindy: 14–17 August 1993". Storm Wallet for Tropical Storm Cindy, 1993 (Preliminary Report). National Hurricane Center. p. 2. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ Roth, David M. (January 3, 2023). "Tropical Cyclone Point Maxima". Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Data. United States Weather Prediction Center. Retrieved January 6, 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ 1980 Allen: Ouragan. Pluies extrêmes aux Antilles (Report) (in French). Météo-France. n.d. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ Rappaport, Edward N (January 17, 1996). "Hurricane Marilyn: September 12–22, 1995" (PDF). 1995 Atlantic Hurricane Season (Preliminary Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ Sugg (August 19, 1970). "Tropical Storm Dorothy Discussion". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ Marcell Perrusset & Pierre Bouguen (1970). "La Tempête Tropicale Dorothy (Page 2)". Direction de la Meteorologie Nationale: Météorologique du Groupe Antilles-Guyane. Retrieved November 12, 2008.
- ^ Staff Writer (August 20, 1970). "Martinique Lashed by Storm". United Press International. Retrieved November 13, 2008.
- ^ a b c d Staff Writer (August 21, 1970). "Say Dorothy Killed 15 On Islands". United Press International. Retrieved November 13, 2008.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Marcell Perrusset & Pierre Bouguen (1970). "La Tempête Tropicale Dorothy (Page 6)". Direction de la Meteorologie Nationale: Météorologique du Groupe Antilles-Guyane. Retrieved November 12, 2008.
- ^ Marcell Perrusset & Pierre Bouguen (1970). "La Tempête Tropicale Dorothy (Page 8)". Direction de la Meteorologie Nationale: Météorologique du Groupe Antilles-Guyane. Retrieved November 12, 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f Marcell Perrusset & Pierre Bouguen (1970). "La Tempête Tropicale Dorothy (Page 4)". Direction de la Meteorologie Nationale: Météorologique du Groupe Antilles-Guyane. Retrieved November 12, 2008.
- ^ R. H. Simpson & Joseph M. Pelissier (1971). "Atlantic Hurricane Season of 1970" (PDF). American Meteorological Society. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^ a b c Staff Writer (August 23, 1970). "Storm Dorothy Weakens, Still Poses Threat to Caribbean Sea Islands". United Press International. Retrieved November 13, 2008.[permanent dead link]