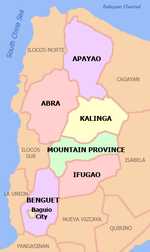
Apayao
Apayao | |
|---|---|
| Province of Apayao | |
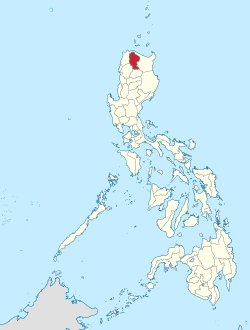 Location in the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 17°45′N 121°15′E / 17.75°N 121.25°E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Cordillera Administrative Region |
| Founded | May 8, 1995 |
| Capital | Kabugao* |
| Administrative center | Luna |
| Largest municipality | Conner |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Elias C. Bulut Jr. (NPC) |
| • Vice Governor | Remy N. Albano (KBL) |
| • Legislature | Apayao Provincial Board |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,413.35 km2 (1,704.00 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 27th out of 81 |
| Highest elevation | 1,921 m (6,302 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 124,366 |
| • Estimate (2020) | 123,898[2] |
| • Rank | 78th out of 81 |
| • Density | 28/km2 (73/sq mi) |
| • Rank | 81st out of 81 |
| Divisions | |
| • Independent cities | 0 |
| • Component cities | 0 |
| • Municipalities | |
| • Barangays | 133 |
| • Districts | Legislative district of Apayao |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PHT) |
| ZIP code | 3807–3814 |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)74 |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-APA |
| Spoken languages | |
| Website | www |
| * Kabugao is the officially recognized capital and seat of government, although the province carries out many of its operations in a new government center established in Luna. | |
Apayao, officially the Province of Apayao (Ilocano: Probinsia ti Apayao; Itawit: Provinsiya ya Apayao; Isnag: Provinsia nga Apayao; Tagalog: Lalawigan ng Apayao), is a landlocked province in the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Kabugao serves as its capital. The provincial capitol and its associated offices are located at the New Government Center in Luna.
The province borders Cagayan to the north and east, Abra and Ilocos Norte to the west, and Kalinga to the south. Prior to 1995, Kalinga and Apayao comprised a single province named Kalinga-Apayao, which was partitioned to better service the needs of individual ethnic groups.
With a population of 124,366 (as of the 2020 census)[3] covering an area of 4,413.35 square kilometres (1,704.00 sq mi),[1] Apayao is the least densely-populated province in the Philippines, the least developed province in Luzon and one of the poorest.
History[edit]
By 20th century, Apayao is predominated by the Isneg people. They are located primarily in the highland municipalities of Kabugao and Calanasan. Majority of them live in scattered settlements along the upper reaches of the Apayao-Abulug River; while some along a major tributary of the Matalag River in Conner.[4]
Spanish colonial era[edit]
Although Apayao which was then part of Cagayan,[5] was among the earliest areas penetrated by the Spaniards in the Cordilleras, the region, inhabited by the Isneg tribe, remained largely outside Spanish control until late in the 19th century. As early as 1610, the Dominican friars established a mission in what is now the town of Pudtol. In 1684, the friars again made attempts to convert the people and established a church in what is now Kabugao.

The Spanish authorities were then able to establish in Cagayan the comandancias of Apayao and Cabugaoan in 1891,[5][6][7] which covered the western and eastern portions of what is now Apayao. The comandancias, however, failed to bring total control and the Spanish government only maintained a loose hold over the area.
American invasion era[edit]
Apayao was established through Act No. 1642 on May 9, 1907 as a sub-province of Cagayan province.[8]
The Americans established the Mountain Province on August 13, 1908, with the enactment of Act No. 1876. Apayao was incorporated; and along with Amburayan, Benguet, Bontoc, Ifugao, Kalinga, and Lepanto, became sub-provinces of this new province.[4][6][7][9]
In the early years, the sub-province underwent series of territorial changes:[10]
- Part of Apayao was transferred to the Province of Ilocos Norte (Executive Order 21, 1920).
- 1922: A barrio of municipal district of Bayag (now Calanasan) was transferred to Namaltugan.
- 1927: Parts of the municipal district of Pinukpuk in Kalinga were annexed to Conner.
- Through EO 200, approved on September 6, 1929, barrios in Tauit were organized into a separate municipal district, Luna, effective October 1.[11]
- Through EO 13, approved on January 21, 1936, Tauit was abolished and was annexed as a single barrio to Luna, effective February 1.[12]
- Through EO 78, approved on December 23, 1936, Namaltugan was abolished and was annexed to Bayag and Kabugao, effective January 1, 1937.[13]
In the early years, Apayao as a sub-province was divided into seven municipal districts, all Isneg predominated.[4]
While the Isneg clashed with the Philippine Constabulary in the early years, the families attempted to escape the area and go into the mountains of Ilocos Norte and Abra. They were involved in an attack in Tauit in 1913.[4]
Japanese occupation era[edit]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (January 2015) |
In 1942, Japanese Imperial forces entered Apayao, starting a three-year occupation of the province during the Second World War.[further explanation needed] Local Filipino troops and the military forces of the 11th and 66th Infantry Regiment, Philippine Commonwealth Army, USAFIP-NL, supported by the Cordilleran guerrillas, drove out the Japanese in 1945.[further explanation needed]
During the Second World War, Kabugao was occupied for a year by the Japanese; an Isneg guerilla force was organized under a United States Army captain who had escaped the Fall of Bataan. Little fighting occurred in the sub-province, but a number of Isneg fought with the American and Filipino forces in the Cagayan Valley and in the neighboring areas. The war and the post-war era seen development among the Isnegs, although slowly.[4]
Postwar Era[edit]
Kalinga-Apayao creation and splitting[edit]
On June 18, 1966, the huge Mountain Province was split into four provinces with the enactment of Republic Act No. 4695. The four provinces were Benguet, Bontoc (renamed "Mountain Province"), Kalinga-Apayao and Ifugao.[7][14] Kalinga-Apayao, along with Ifugao, became one of the provinces of the Cagayan Valley region in 1972.[14]
During the Marcos dictatorship[edit]
The beginning months of the 1970s marked a period of turmoil and change in the Philippines, as well as in Kalinga-Apayao.[15] During his bid to be the first Philippine president to be re-elected for a second term, Ferdinand Marcos launched an unprecedented number of foreign debt-funded public works projects. This caused[16][17] the Philippine economy took a sudden downwards turn known as the 1969 Philippine balance of payments crisis, which in turn led to a period of economic difficulty and social unrest.[18][19] : "43" [20][21]
With only a year left in his last constitutionally allowed term as president Ferdinand Marcos placed the Philippines under Martial Law in September 1972 and thus retained the position for fourteen more years.[22] This period in Philippine history is remembered for the Marcos administration's record of human rights abuses,[23][24] particularly targeting political opponents, student activists, journalists, religious workers, farmers, and others who fought against the Marcos dictatorship.[25] The Kalinga-Apayao became known as a flashpoint of conflict between the Marcos dictatorship and the various indigenous peoples who lived in the area, because of the Chico River Dam Project,[26][27] which, even if only the most essential part of it were built, would have submerged numerous townships in Kalinga, Mountain Province, and Apayao;[28] and would have displaced about 100,000 indigenous people.[29] Marcos sent three armed brigades to subdue protests, resulting in heightened tensions in the area.[27]
Apayao was deeply affected by events that took place in its sister sub-province of Kalinga, as well as the neighboring provinces of Abra and Mountain Province (Bontoc, including the struggle against the Chico Dam Project, the struggle against the encroachment on indigenous lands of logging company Cellophil Resources Corporation owned by Marcos crony Herminio Disini, and the rise of multiple armed Cordilleran autonomy movements.[26][28]
After the People Power Revolution[edit]
After Marcos was finally deposed by the civilian-led People Power Revolution in 1986, many of the activists who had joined the underground movement decided to "surface," as the new administration of Corazon Aquino released political prisoners and initiated peace talks.[30] However, anti-left sentiment in Aquino's new cabinet, which included figures who had sided witht he Reform the Armed Forces Movement, made the peace process difficult, and negotiations eventually collapsed, and the insurgency in Kalinga-Apayao persisted.[31][32]
Another event in 1986 marked the beginning of political change in the region, however - the splitting of the Cordillera People's Liberation Army from the New People's Army. Former Catholic priest Conrado Balweg, who had left his calling and joined the NPA in 1979, had been having disagreements with the NPA leadership over tactics and objectives in the Cordillera for four years when he finally decided to split from the NPA in early April 1986,[33]believing that Igorot interests were better served through regional struggles for liberation, rather than the national-scale conflict pursued by the NPA.[34]. Either way, this set the stage for negotiations which would eventually lead to the creation of the Cordillera Administrative Region, and Apayao as an independent province within it.
Peace accord and creation of the Cordillera Administrative Region creation[edit]
In September 1986, the CPLA signed the Mount Data Peace Accord with the government, which led to the creation of what became called the Cordillera Autonomous Region, although attempts to ratify actual autonomy in the region have failed due to non-ratification during plebiscites.[35][36]
The Cordillera Administrative Region was established on July 15, 1987, and Kalinga-Apayao was made one of its provinces.[7][14][37][38]
Finally, on February 14, 1995, Kalinga-Apayao was split into two independent provinces with the passage of Republic Act No. 7878.[7][14][39]
Geography[edit]

Apayao is basically situated within the Cordillera Central mountains, traversed by many rivers. The province covers an area of 4,413.35 square kilometres (1,704.00 sq mi)[40] forming the northern tip of the Cordillera Administrative Region, and is bounded on the north and east by Cagayan, west by Ilocos Norte, southwest by Abra and south by Kalinga.
The province is geographically subdivided into Upper Apayao (composed of the upland municipalities: Calanasan, Conner and Kabugao) and Lower Apayao (the lowland municipalities: Luna, Pudtol, Flora and Sta. Marcela).[41]
Plains and valleys are used for farming. Apayao is basically composed of farmlands.[citation needed]
Climate[edit]
The prevailing climate in the province falls under Corona's Type III Classification. It is characterized by relatively dry and wet seasons, from November to April, and wet during the rest of the year. Heaviest rain during December to February while the month of May is the warmest.
Biodiversity[edit]
Apayao is biologically diverse. The province is sanctuary to 139 bird species, 61 of which are endemic and 4 threatened.[42] It also has 43 species of wild food plants eaten by the indigenous people and 50 species of medicinal plants.[43] The province is home to critically endangered rufous hornbills, lawaan or dipterocarp trees, Raflesia flowers, and the white-winged flying fox.[42]
The Philippine Eagle Foundation began its search of eagles in Apayao in 2011 after reports of huge eagles were roaming the area for centuries.[44] On March 22, 2013, scientists discovered the stronghold of critically endangered Philippine eagles, the country's national bird, in Luzon island within the vicinity of the Calanasan Lowland Forest.[45] In January 2015, the town of Calanasan initiated a program which protected 3,000 hectares of forests under its jurisdiction.[46] Additionally, the province of Apayao is one of the very few in the country that has an approved forest land use plan (FLUP).[47] The first active Philippine eagle nest in Apayao was discovered in July 2015.[44]
Biosphere reserve[edit]
On 9 July 2018,[47] the provincial government of Apayao announced their intent for the province to be a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. The province, which possesses more than 286,000 hectares of virgin forests, also noted that they have sent four of their personnel to train in the United States under the US Foreign Service to hasten the declaration of the site.[48] On January 16, 2019, the provincial government announced that they were doing "legwork for the inscription."[49]
Administrative divisions[edit]
Apayao comprises 7 municipalities, all encompassed by a lone legislative district.[40]

|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Barangays[edit]
The 7 municipalities of the province comprise a total of 133 barangays, with Barangay Malama in Conner as the most populous in 2015, and Eleazar in Calanasan as the least.[51][40]
Demographics[edit]
The population of Apayao in the 2020 census was 124,366 people,[50] with a density of 28 inhabitants per square kilometre or 73 inhabitants per square mile.
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1918 | 9,787 | — |
| 1939 | 15,614 | +2.25% |
| 1948 | 19,357 | +2.42% |
| 1960 | 29,601 | +3.60% |
| 1970 | 49,652 | +5.30% |
| 1975 | 61,115 | +4.25% |
| 1980 | 70,681 | +2.95% |
| 1990 | 74,720 | +0.56% |
| 1995 | 83,660 | +2.14% |
| 2000 | 97,129 | +3.25% |
| 2007 | 103,633 | +0.90% |
| 2010 | 112,636 | +3.08% |
| 2015 | 119,184 | +1.08% |
| 2020 | 124,366 | +0.84% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[52][53] | ||

Based on the 2000 census survey, Ilocanos comprised 49,328 (50.82%) of the total provincial population of 97,058, while almost 1/3 of the population were Isnag at 29,071 (29.95%). Other ethnic groups in the province were the Malaueg at 3,580 (3.69%), Isneg at 3,380 (3.48%), Kalinga at 2,992 (3.08%), Kankanaey at 1,208 (1.24%), Bontoc at 1,014 (1.04%), and Ibaloi at 979 (1.01%).[54]
Economy[edit]
Apayao is devoted to agricultural production, particularly food and industrial crops such as palay,[63] corn,[64] coffee, root crops and vegetables. Fruits produced include lanzones, citrus, bananas and pineapples, durian, santol, rambutan, coconut and mangosteen.[65] Rice production totaled 98,489 metric tons in 2011.[63] Parts of Apayao are home to rice terraces.[66]
Economic activity is also based on livestock and poultry breeding such as swine, carabao, cattle, goat and sheep. Other additional investment includes manufacturing, food processing, furniture, crafts and house wares making.[67]
Updated records of the Department of Trade and Industry Provincial Office reveal that existing industries in the province are furniture, garment craft, food processing, gifts and house wares, and agricultural support.
The people of Apayao also have a rich tradition of basket, handicraft, and textile weaving.[68]
Tauit[edit]
Tauit (or Tawit), an Isneg settlement along the lower Apayao-Abulug River, was a former municipal district and Apayao's first sub-provincial capital (1907–1915) until the capital was moved to Kabugao in August 1915 by virtue of Executive Order No. 45.[4][8][10][69] It had been existed by the time of creation of the sub-province of Apayao.[70]
Tauit is said to be the forerunner of the present-day Pudtol.[71][72] Its seat of government at Barrio Tawit was later divided into four barangays in the municipality.[70][73]
In 1913, a band of Isneg attacked Tauit, as they were infuriated by the large number of Ilocano settling in the territory under the protection of the local government.[4]
In 1926, Allacapan was founded as its municipal district. In July 1927, the area was separated from Tauit and was organized into an independent one with the same name by virtue of EO No. 68.[10] It was ceded to the province of Cagayan in 1928.[74]
In 1929, a separate municipal district taken from Tauit, Macatel (later renamed Luna through a resolution), was organized through EO No. 200.[70][73][75]
Difficulties in transportation led to the decision to abandon Tauit as a municipal district and to be represented by Luna.[73]
Tauit was abolished through EO No. 13, issued on January 21, 1936 and effective February 1, with remaining territories annexed as a single barrio to Luna.[12][73] These territories were established as the municipal district of Pudtol upon its creation on December 3, 1956 through EO No. 217.[70][76]
Parts of the territories of Pudtol and Luna were later established as the municipalities of Flora and Santa Marcela; meanwhile, Tauit also comprised some parts of Lasam in Cagayan. At present, remnants of Tauit are located in northeastern Apayao and in few parts of Cagayan.[70][71][73]
References[edit]
- ^ a b "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Archived from the original on 19 April 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ "POPULATION PROJECTIONS BY REGION, PROVINCE, CITIES AND MUNICIPALITIES, 2020-2025". www.doh.gov.ph. Department of Health. August 27, 2020. Archived from the original on May 14, 2021. Retrieved October 16, 2020.
- ^ a b Census of Population (2020). Table B - Population and Annual Growth Rates by Province, City, and Municipality - By Region. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g "The Manolay cult: The genesis and dissolution of millenarian sentiments among the Isneg of Northern Luzon" (PDF). Asian Studies. University of the Philippines Diliman. Retrieved 2022-07-31.
- ^ a b "History". Province of Cagayan (Official Website of the Provincial Government of Cagayan). Retrieved 18 January 2015.
- ^ a b "Benguet History". Province of Benguet (official website). Archived from the original on 19 October 2014. Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Historical Background". Provincial Government of Apayao (official website). Archived from the original on 4 January 2015. Retrieved 18 January 2015.
- ^ a b "Act No. 1642". Supreme Court E-Library. Government of the Philippines. 1907-05-09. Retrieved 2022-07-24.
- ^ Ingles, Raul Rafael (2008). 1908 :The Way it Really was : Historical Journal for the UP Centennial, 1908-2008. Diliman, Quezon City: University of the Philippines Press. p. 330. ISBN 978-9715425803. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ a b c "Index to Official Gazette (1913–1928)" (PDF). University of San Carlos. The Library Corporation. 2011–2012. Retrieved 2022-07-31.
—Executive Order 45 (1915): Executive Orders, 1915. Manila: Bureau of Printing. 1916. pp. 91–92. Retrieved 2022-08-02.
—Executive Order 68 (1927): Executive Orders, 1927. Manila: Bureau of Printing. 1928. pp. 48–50. Retrieved 2022-08-02. - ^ Executive Orders and Proclamations, 1929. Manila: Bureau of Printing. 1930. pp. 81–83. Retrieved 2022-08-05.
- ^ a b "Executive Order No. 13, s. 1936" Official Gazette. Retrieved July 26, 2022.
- ^ "Executive Order No. 78, s. 1936". Official Gazette. Government of the Philippines. 1936-12-23. Retrieved 2022-07-26.
- ^ a b c d Lancion, Jr., Conrado M.; de Guzman, Rey (cartography) (1995). "The Provinces". Fast Facts about Philippine Provinces (The 2000 Millenium ed.). Makati, Metro Manila: Tahanan Books. pp. 76, 86, 108. ISBN 971-630-037-9. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ Robles, Raissa (2016). Marcos Martial Law: Never Again. Filipinos for a Better Philippines, Inc.
- ^ Balbosa, Joven Zamoras (1992). "IMF Stabilization Program and Economic Growth: The Case of the Philippines" (PDF). Journal of Philippine Development. XIX (35). Archived from the original (PDF) on September 21, 2021. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ Balisacan, A. M.; Hill, Hal (2003). The Philippine Economy: Development, Policies, and Challenges. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195158984.
- ^ Cororaton, Cesar B. "Exchange Rate Movements in the Philippines". DPIDS Discussion Paper Series 97-05: 3, 19.
- ^ Kessler, Richard J. (1989). Rebellion and repression in the Philippines. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 0300044062. OCLC 19266663.
- ^ Celoza, Albert F. (1997). Ferdinand Marcos and the Philippines: The Political Economy of Authoritarianism. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 9780275941376.
- ^ Schirmer, Daniel B. (1987). The Philippines reader : a history of colonialism, neocolonialism, dictatorship, and resistance (1st ed.). Boston: South End Press. ISBN 0896082768. OCLC 14214735.
- ^ Magno, Alexander R., ed. (1998). "Democracy at the Crossroads". Kasaysayan, The Story of the Filipino People Volume 9:A Nation Reborn. Hong Kong: Asia Publishing Company Limited.
- ^ "Alfred McCoy, Dark Legacy: Human rights under the Marcos regime". Ateneo de Manila University. September 20, 1999.
- ^ Abinales, P.N.; Amoroso, Donna J. (2005). State and society in the Philippines. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. ISBN 978-0742510234. OCLC 57452454.
- ^ "Gone too soon: 7 youth leaders killed under Martial Law". Rappler. Retrieved June 15, 2018.
- ^ a b Doyo, Ma. Ceres P. (2015). Macli-ing Dulag: Kalinga Chief, Defender of the Cordillera. Diliman, Quezon City: University of the Philippines Press. ISBN 978971542772-2.
- ^ a b Joanna K. Cariño, "The Chico River Basin Development Project: A Case Study in National Development Policy," Aghamtao Vol. III (December 1980): 2, https://pssc.org.ph/wp-content/pssc-archives/Aghamtao/1980/05_The%20Chico%20River%20Basin%20Development%20Project_%20A%20Case%20Study%20in%20National%20Development%20Policy.pdf.
- ^ a b https://hrvvmemcom.gov.ph/remembering-macli-ing-dulag/
- ^ "Valley of Sorrow". Asiaweek. 1980-09-05.
- ^ Villegas, Bernardo M. (1987-02-01). "The Philippines in 1986: Democratic Reconstruction in the Post-Marcos Era". Asian Survey. 27 (2): 194–205. doi:10.2307/2644614. ISSN 0004-4687. JSTOR 2644614.
- ^ Curaming, Rommel and Claudio, Lisandro, A Historicised (Re)Assessment of EDSA 'People Power' (1986) (February 1, 2010). Asia Research Institute Working Paper No. 134. https://ssrn.com/abstract=1716572 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1716572
- ^ Marchadesch, Barbara (November 24, 2017). "TIMELINE: The peace talks between the government and the CPP-NPA-NDF, 1986 – present". GMA News Online. Archived from the original on November 24, 2017. Retrieved April 15, 2020.
- ^ https://peace.gov.ph/timeline/peace-process-cba-cpla/
- ^ https://www.insights-philippines.de/balwegengl.htm
- ^ Amor, Patria (February 4, 1990). "What now for Cordillera?". The Manila Standard. Retrieved June 11, 2020.
- ^ Maragay, Fel V. (1990-02-01). "Cordillerans reject autonomy proposal". news.google.com. Manila Standard. Retrieved 2020-06-22.
- ^ "Regional Profile: Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)". CountrySTAT Philippines. Archived from the original on 22 October 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ "The Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)". Department of Agriculture. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ "Republic Act No. 7878 - An Act Converting the Sub-provinces of Kalinga and Apayao into Regular Provinces to be Known as the Province of Kalinga and the Province of Apayao, Amending for the Purpose Republic Act No. 4695". Chan Robles Virtual Law Library. Retrieved 18 January 2015.
- ^ a b c d "Province: Apayao". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ "Apayao: Executive Summary, 2015" (PDF) Commission on Audit. Retrieved Aug. 4, 2022.
- ^ a b Ranada, Pia (July 23, 2015). "Apayao: Where ethnic tradition is saving the Philippine Eagle". Rappler. Retrieved 2020-06-21.
- ^ Angagan, J. (2009). "Indigenous knowledge and biodiversity conservation practices in Apayao rice terraces [Philippines]: a gender lens perspective". Journal of ISSAAS [International Society for Southeast Asian Agricultural Sciences] (Philippines).
- ^ a b Ranada, Pia (July 14, 2015). "First active Philippine eagle nest in Luzon found in Apayao". Rappler. Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ "Eagle Sightings in Apayao". philippineeaglefoundation.org. Archived from the original on 2019-02-27. Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ "Bayanihan.org". bayanihan.org.
- ^ a b Dumlao, Artemio (July 9, 2018). "Apayao eagle habitat eyed as Unesco protected area". The Philippine Star. Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ "Gov Bulut wants Calanasan Philippine Eagle sanctuary declared as protected area | Politiko North Luzon". July 27, 2018.
- ^ Geminiano, Pamela Mariz (January 16, 2019). "Apayao eyes UNESCO biosphere reserve title to save PH eagles". Philippines News Agency. Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ a b Census of Population (2020). "Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ a b Census of Population (2015). "Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population (2015). Highlights of the Philippine Population 2015 Census of Population. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities (PDF). National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ a b "Apayao: Three Out of Five Academic Degree Holders Were Females; Table 4. Household Population by Ethnicity and Sex: Apayao, 2000". Philippine Statistics Authority. 12 July 2002. Archived from the original on 9 June 2006. Retrieved 17 December 2015.
- ^ "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- ^ "Estimation of Local Poverty in the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 29 November 2005.
- ^ "2009 Official Poverty Statistics of the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 8 February 2011.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 27 August 2016.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 27 August 2016.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 27 August 2016.
- ^ "Updated Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population with Measures of Precision, by Region and Province: 2015 and 2018". Philippine Statistics Authority. 4 June 2020.
- ^ "2021 Full Year Official Poverty Statistics of the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 15 August 2022. Retrieved 28 April 2024.
- ^ a b "DA allots P278M for irrigation, agri projects in Apayao". Official Gazette of the Republic of the Philippines. Department of Agriculture. 15 June 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
Last year, Apayao produced a total of 98,489 metric tons of palay (paddy rice), according to the DA's Bureau of Agricultural Statistics. The volume is equivalent to 64,017 MT of rice at 65 percent milling recovery.
- ^ Vanzi, Sol Jose (28 April 1998). "Apayao Secret: Drought-Resistant Corn". Newsflash.Org. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ Galvez, James Konstantin (14 January 2014). "Government agri program to promote Apayao's wild fruits". The Manila Times. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
The province of Apayao is host to some of the country's indigenous crops including: lubeg, bignay, bignay kalabaw, calumpit, saging matsing, other than the fruit-bearing trees like durian, marang, lanzones, rambutan, pineapple, mangosteen, coconut, santol, among others.
- ^ Malingan, Jamie Joie. "Survival and Identity: The Cordillera Rice Terraces in the 21st century". pia.gov.ph. Retrieved 2020-06-21.
- ^ "Apayao producers open new markets in cities". Philippine Information Agency. 5 December 2009. Archived from the original on 20 May 2018. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ Ocampo, R. O. (2009). "Tapping the potentials of the weaving industry in Apayao [Philippines]". Journal of ISSAAS [International Society for Southeast Asian Agricultural Sciences] (Philippines).
- ^ Report of the Philippine Commission to the Secretary of War, 1908. Washington, D.C.: US Government Printing Office. 1909. pp. 266–269. Retrieved 2022-08-01.
- ^ a b c d e Pudtol - A Brief History Retrieved July 26, 2022.
- ^ a b "Brief History of Pudtol" Municipality of Pudtol. Retrieved Aug. 1, 2022.
- ^ "Pudtol: Executive Summary, 2020" (PDF) Commission on Audit. Retrieved Aug. 1, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e History and government of Luna, Apayao (via Department of the Interior and Local Government–CAR). Retrieved July 28, 2022.
- ^ "Municipalities: Allacapan" CagayaNET. 1997–1998. Retrieved 08-01-2022.
- ^ "Brief History" Municipality of Luna, Apayao. Retrieved July 28, 2022
- ^ "Executive Order No. 217, s. 1956" Official Gazette. Retrieved Aug. 1, 2022.
External links[edit]
 Media related to Apayao (province) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Apayao (province) at Wikimedia Commons Geographic data related to Apayao at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Apayao at OpenStreetMap