Beresteishchyna
| Beresteishchyna Берестейщина (Ukrainian) Берасцейшчына (Belarusian) | |
|---|---|
 Various proposed borders between the Ukrainian and Belarusian languages in southwestern Belarus/northwestern Ukraine | |
| Capital | Brest |
| Today part of | |
Beresteishchyna (Ukrainian: Берестейщина; Belarusian: Берасцейшчына, romanized: Byerastsyeyshchyna) is a region in Western Polesie, in what is primarily the modern Brest Region of Belarus. Located along the western Bug.
Name
[edit]Other names for Beresteishchyna include Brest Land, Brest Volost, Berestiyshchyna,[1] Brestshchyna,[2] Brest Krai, and Polissia.[3]
History
[edit]Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
[edit]During the time of the Union of Lublin, representatives from Beresteishchyna and Volhynia spoke in favour of unification with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, alongside other Ukrainian lands.[4]
Later, the Ukrainians of Beresteishchyna became involved in Cossack uprisings. During the Khmelnytsky Uprising, there was a pro-Khmelnytsky uprising in Brest, which lasted for over three months, from September 1648 to January 1649, before being crushed by the forces of Janusz Radziwiłł. Another uprising occurred in 1649, leading to the deaths of approximately 2,000 of the city's residents. Other, more minor uprisings took place in Turov, Ivanava, and Kobryn.[5]
Russian Empire
[edit]
Following the partitions of Poland, Beresteishchyna became part of the Russian Empire. In the 1860s, Ukrainian ethnographer Pavlo Chubynsky made two visits to the region. Twenty years later, Ukrainian theatre began to organise in the region.[6] By the turn of the century, an estimated 800,000 to 1 million Ukrainians lived in the region.[7] In 1914, the State Duma passed a law including southern parts of Beresteishchyna into the Kholm Governorate, part of the Southwestern Krai.
During World War I, Beresteishchyna was occupied by the German Empire. The Russian Empire deported Ukrainian, Belarusian, and Polish residents alike to the Far East as part of their deportations of residents from the western regions of the country.[8][9] In 1916, the first branch of the Prosvita society in Polesia was founded in Brest. The next year, the first ever conference of teachers from throughout Ukraine was held in the village of Dyvin.[10]
Russian Civil War
[edit]According to the terms of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk signed between the Ukrainian People's Republic and the Central Powers, Ukraine gained Beresteishchyna, Chełm Land, and Podlachia.[11] The Ukrainian People's Republic established a new Kholm Governorate, including Brest as its capital and headed by Oleksandr Skoropys-Yoltukhovskyi.[12] The Ukrainian State that succeeded the Ukrainian People's Republic established the Polissia Okruha, with plans to include it into the Volhynian Governorate.[11] The government of Ukraine at the time had plans to open a total of 320 Ukrainian-language schools in the Okruha, and Ukrainian studies courses were created.[10] Several Ukrainian-language newspapers also existed in the city.[1]
During the autumn of 1918, a Bolshevik uprising began in Polesia, centred around Luninets, Dubrovytsia, and Sarny.[12] This uprising was followed by the handover of the region to the re-established Ukrainian People's Republic by the Germans,[1] and the subsequent entrance of the Polish Army as part of the Polish–Soviet War.[10]
Interwar period
[edit]
According to the Peace of Riga, Beresteishchyna was included into the Second Polish Republic, and became the Polesie Voivodeship. In the 1922 Polish legislative election, three ethnically-Ukrainian deputies from Polesie Voivodeship were elected: Vasyl Dmytriyuk, Serhiy Khrutskyi, and Ivan Pasternak.[13] During the interwar period, Ukrainian nationalist activities actively continued; the Ukrainian National Democratic Alliance, Ukrainian Women's Union, Volhynian Ukrainian Association, Ukrainian Workers' and Peasants' Socialist Alliance, and Sel-Soiuz were all active in the region.[8][13] In 1923, Prosvita reopened in Brest, and soon spread throughout the region, including 127 villages by 1929. A branch of the Ukrainian secret society Ridna Khata existed in the region from December 1929.[10] By 1926, this activity had culminated into at least 480 villages in Polesie Voivodeship appealing to the Polish government to open Ukrainian-language schools in their respective villages.[14] Prosvita was banned in 1935, though it continued to operate illegally until 1938.[1][10][15]
The Polish government, however, undertook a series of Polonization campaigns. The countryside was settled with osadnicy, Eastern Orthodox churches were destroyed as part of the Revindication, and the Bereza Kartuska Prison operated in the region. These activities strengthened the position of Ukrainian nationalist groups in the region, such as the Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists and the Communist Party of Western Ukraine.[15] A 3–4 July 1933 demonstration by peasants in Kobryn County in support of the CPWU was broken up by the Polish police.[6] In January 1939, the Polesian Lozove Cossacks, a pro-OUN guerrilla movement, formed around the area of Ivanava.[16]
World War II and post-war period
[edit]
As part of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Polesie Voivodeship was annexed by the Soviet Union following the invasion of Poland. Polesie Voivodeship was included into the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, with the exception of Koszyr County, which became part of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic.[17] Following the annexation, there were protests in Brest and Kobryn by residents, who asked to join the Ukrainian SSR. A Polesian delegation went to the People's Congress of Western Ukraine, but was denied the right to participate by the Soviet government.[18] Nikita Khrushchev, then First Secretary of the Communist Party of Ukraine, also supported the inclusion of the region into Ukraine, but was denied by Joseph Stalin in favour of Panteleimon Ponomarenko, First Secretary of the Communist Party of Byelorussia.[19] After the region's annexation into the Byelorussian SSR, an active campaign of de-Ukrainisation and Russification began, with Ukrainian-language schools being closed and the Russian language being introduced. By 1940, there were 58 Ukrainian-language schools in Brest Region,[20] though this number later decreased to 30.[21]
After Operation Barbarossa, Beresteishchyna was included into Reichskommissariat Ukraine by Nazi Germany. Local OUN committees were established in Kobryn, Zhabinka, Ivanava, Dyvin, and Drohiczyn.[22] Ukrainian-language newspapers once again began publishing,[1] and 159 Ukrainian-language schools were operating in Beresteishchyna by February 1943.[20] In 1941, the Ukrainian People's Revolutionary Army, led by Taras Bulba-Borovets, formed in Polesia. The first Beresteishchyna sotnia of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army formed in Dyvin in October 1942, eventually growing into two military districts within Beresteishchyna: 1 and 3, both part of UPA-North.[23] Ukrainian insurgent groups engaged in combat with both Soviet Belarusian partisans and the Polish resistance, as well as with German forces. By late 1944, 840–1,200 UPA soldiers were active in Beresteishchyna.[24]
After the end of the war, the Soviets cracked down on the UPA. By May or June 1948, the Beresteishchyna command had been destroyed.[24] The final UPA-Soviet confrontations in the region took place in Ivanava District and Kobryn District in March 1952 and 1953, respectively, both of which ended in defeats for the UPA.[23]
Since 1990
[edit]The early 1990s, with the independence of Belarus, led to increased activity from Belarusian Ukrainians.[1] On 18 February 1990, the Ukrainian Public Civic Association of Brest Region was formed, advocating for granting Ukrainians in Beresteishchyna the status of a national minority and working for the preservation of their culture.[2] The Ukrainian-language newspaper Voice of Beresteishchyna was published from 1991 to 1996, and the Beresteishchyna Prosvita organisation was founded.[1] In 1996, the Beresteishchyna Dictionary was published by Volodymyr Leoniuk in Lviv.[25] The same year, Ukrainian studies began being offered as a course at A.S. Pushkin Brest State University.
However, this expression of Ukrainian cultural identity was not welcomed by the Belarusian population. In 1990, the militsiya attacked members of the Ukrainian Public Civic Association as they were selling newspapers, referring to them as "Banderites", and telling them to, "go back to Lvovshchina".[26] In addresses to the Supreme Council of Belarus, head of the State Security Committee Eduard Shyrkouski made disparaging remarks about the Public Civic Association. Viktor Sheiman, also head of the State Security Committee, declared a total ban on the Ukrainian movement in Brest Region, comparing the situation to Kosovo. On 7 April 1999, Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko claimed that a Polish-Ukrainian congress would be held in Brest demanding autonomy,[27] and subsequently banned the Beresteishchyna Dictionary and the Beresteishchyna Prosvita.[20]
Demographics
[edit]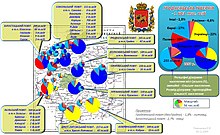
According to the Russian Empire census of 1897, Ukrainian was the most spoken language of the region; Brestsky Uyezd had a Ukrainian-speaking population of 140,561 (64.4%), while Kobrinsky Uyezd had a Ukrainian-speaking population of 146,789 (79.6%).
| Language | Speakers | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Ukrainian | 140,561 | 64.4% |
| Jewish | 45,397 | 20.8% |
| Russian | 17,759 | 8.1% |
| Polish | 8,515 | 3.9% |
| Belarusian | 3,997 | 1.8% |
| Language | Speakers | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Ukrainian | 146,789 | 79.6% |
| Jewish | 25,307 | 13.7% |
| Russian | 5,746 | 3.1% |
| Polish | 4,148 | 2.2% |
| Belarusian | 1,563 | 0.8% |
| Language | Speakers |
|---|---|
| Ukrainian | 287,350 |
| Jewish | 70,704 |
| Russian | 23,505 |
| Polish | 12,663 |
| Belarusian | 5,560 |
During the Second Polish Republic, the number of Ukrainians decreased and the number of Belarusians and Tutejszy increased. According to Ukrainian anthropologist and nationalist politician Volodymyr Kubijovyč, this was due in part to the recording of Ukrainians as Belarusians in spite of their answers.[30]
| Nationality/language | Population, 1921[a] | Percentage, 1921 | Population, 1931[a] | Percentage, 1931 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tutejszy | 36.8 | 4.9% | 707.1 | 62.3% |
| Poles | 191.5 | 25.6% | 164.4 | 14.5% |
| Jews | 80.4 | 10.7% | 113 | 10.0% |
| Belarusians | 361.5 | 48.4% | 73.4 | 6.6% |
| Ukrainians | 73.4 | 9.8% | 54.0 | 4.8% |
| Russians | 3.6 | 0.5% | 16.2 | 1.4% |
| Other | 0.3 | 0.1% | 2.1 | 0.2% |
The 2009 Belarusian census recorded a total of 158,723 Ukrainians in Belarus, with 40,046 (25.2%) of these Ukrainians being in Brest Region.[31] This was a decrease from the 1999 Belarusian census, where the Ukrainian population was 57,111.[25] Estimates from Ukrainian observers consider the actual number to be far higher - around one million people.[32]
Notable people
[edit]- Athanasius of Brest, hieromartyr and saint of the Orthodox Church
- Natalka Babina, Belarusian Ukrainian-language writer
- Mykhailo Krychevsky, Polish noble and Cossack commander
- Kazimierz Łyszczyński, Polish philosopher
- Theodore Odrach, Ukrainian writer
- Hypatius Pociej, Metropolitan of Kiev, Galicia and all Ruthenia
- Oleksa Storozhenko, Ukrainian writer, anthropologist, playwright
- Volodymyr Vasylkovych, Belarusian noble
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g Isayevych, Yaroslav; Leoniuk, Volodymyr. Берестейщина [Beresteishchyna] (in Ukrainian). ISBN 9789660220744. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ a b Довідник з історії України [Handbook on the History of Ukraine] (in Ukrainian). Kyiv: Heneza. 1993. p. 37.
- ^ Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. p. 65. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. pp. 15, 350. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. pp. 17, 351. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ a b Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. pp. 308, 353. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ Arkushyn, Hryhoriy (2015). "Українська більшість Берестейщини як сучасна меншість" [The Ukrainian majority of Beresteishchyna as a modern minority] (PDF). Volyn-Zhytomyr Historical and Philological Collection of Regional Issues (in Ukrainian): 6.
- ^ a b Hrytsenko, Halyna. "Культурно-просвітницька діяльність українців і білорусів у міжвоєнний період" [Ukrainian and Belarusian cultural and educational figures during the interwar period] (PDF). Humanitarian Science Issues: 36–42.
- ^ Arkushyn, Hryhoriy (2015). "Українська більшість Берестейщини як сучасна меншість" [The Ukrainian majority of Beresteishchyna as a modern minority] (PDF). Volyn-Zhytomyr Historical and Philological Collection of Regional Issues (in Ukrainian): 7.
- ^ a b c d e "Олександр Вабіщевич. УКРАЇНСЬКИЙ КУЛЬТУРНО-ПРОСВІТНИЦЬКИЙ РУХ НА ПОЛІССІ (1920—30-ті рр.)" [Oleksandr Vabishchevych: The Ukrainian cultural-education movement in Polesia (1920s-1930s)]. Union of Belarusian Writers. Archived from the original on 19 January 2021. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ a b Isayevych, Yaroslav (2003). "Берестейська земля, Берестейщина" [Brest Land, Beresteishchyna]. Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine (in Ukrainian). Kyiv: Institute of History of Ukraine.
- ^ a b Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. p. 355. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ a b Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. p. 27. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ Serhiychuk, Volodymyr (2008). Етнічні межі і державний кордон України [Ethnic boundaries and state borders of Ukraine] (in Ukrainian) (3 ed.). Kyiv. pp. 101, 497. ISBN 9789662911244.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. p. 28. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. pp. 28, 356. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^
 Указ Президиума ВС СССР от 4.12.1939 о разграничении областей между Украинской ССР и Белорусской ССР [4.12.1939 Order by the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR on delimitation of regions between the Ukrainian SSR and the Byelorussian SSR (in Russian). Wikisource. Accessed 30 April 2023.
Указ Президиума ВС СССР от 4.12.1939 о разграничении областей между Украинской ССР и Белорусской ССР [4.12.1939 Order by the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR on delimitation of regions between the Ukrainian SSR and the Byelorussian SSR (in Russian). Wikisource. Accessed 30 April 2023.
- ^ Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. pp. 29, 356. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ Makarchuk, Stepan (2008). Етнічна історія України [Ethnic History of Ukraine] (in Ukrainian). Kyiv: Znannia. p. 221. ISBN 9789663464091.
- ^ a b c Vynnychenko, Ihor (4 June 1999). "Українці Берестейщини - автохтони чи іммігранти?" [Beresteishchyna Ukrainians - autochthonous or immigrants?]. The Day (Kyiv) (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 13 January 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ Serhiychuk, Volodymyr (2008). Етнічні межі і державний кордон України [Ethnic boundaries and state borders of Ukraine] (in Ukrainian) (3 ed.). Kyiv. p. 502. ISBN 9789662911244.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Serhiychuk, Volodymyr (2008). Етнічні межі і державний кордон України [Ethnic boundaries and state borders of Ukraine] (in Ukrainian) (3 ed.). Kyiv. p. 381. ISBN 9789662911244.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. pp. 30, 308. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ a b Serhiychuk, Volodymyr (2008). Розвиток українського визвольного руху на Берестейщині в роки Другої світової війни як вияв національного відродження [The development of the Ukrainian liberation movement in Beresteishchyna during the Second World War as a manifestation of national revival] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: I. Krypyakevych Institute of Ukrainian Studies of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. pp. 384–389.
- ^ a b Makarchuk, Stepan (2008). Етнічна історія України [Ethnic History of Ukraine] (in Ukrainian). Kyiv: Znannia. p. 222. ISBN 9789663464091.
- ^ Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. p. 357. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ Leoniuk, Volodymyr (1996). Словник Берестейщини [Beresteishchyna Dictionary] (in Ukrainian). Lviv: Afisha. pp. 109, 187–188. ISBN 9669506301.
- ^ "Брестский уезд". Demoscope (in Russian). Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ "Кобринский уезд". Demoscope (in Russian). Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ a b Kubijovyč, Volodymyr (1963). Західні Українські Землі в межах Польщі 1920-1939 [Western Ukraine Within Poland 1920-1939] (in Ukrainian). Chicago, New York: Ukrainian Scientific Publishing Institute. pp. 22–23.
- ^ "Ethnic composition of Belarus 2009". pop-stat.mashke.org. 14–24 October 2009. Archived from the original on 14 January 2016. Retrieved 19 March 2022.
- ^ Serhiychuk, Volodymyr (2008). Етнічні межі і державний кордон України [Ethnic boundaries and state borders of Ukraine] (in Ukrainian) (3 ed.). Kyiv. p. 494. ISBN 9789662911244.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)


