Caño Tomás Fault
| Caño Tomás Fault | |
|---|---|
| Falla de Caño Tomás | |
| Etymology | Caño Tomás |
| Named by | Page |
| Year defined | 1986 |
| Coordinates | 8°26′N 73°17′W / 8.433°N 73.283°W |
| Country | |
| Region | Andean |
| State | Norte de Santander |
| Characteristics | |
| Range | Eastern Ranges, Andes |
| Part of | Andean thrust faults |
| Length | 81.6 km (50.7 mi) |
| Strike | 011.4 ± 8 |
| Dip | West |
| Dip angle | High |
| Displacement | <0.2 mm (0.0079 in)/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | North Andean |
| Status | Inactive |
| Type | Thrust fault |
| Movement | Reverse |
| Age | Quaternary |
| Orogeny | Andean |
The Caño Tomás Fault (Spanish: Falla de Caño Tomás) is a thrust fault in the department of Norte de Santander in northern Colombia. The fault has a total length of 81.6 kilometres (50.7 mi) and runs along an average north-northeast to south-southwest strike of 011.4 ± 8 in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
Etymology
[edit]The fault is named after Caño Tomás a vereda of Teorama.[1]
Description
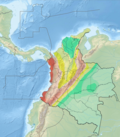
[edit]The fault with a total length of 81.6 kilometres (50.7 mi) is located about 50 kilometres (31 mi) to the west of the town of Tibú, Norte de Santander, along the eastern base of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. In the northern part, the fault places agglomerates and breccias of Jurassic to Triassic age against shales and sandstones of Cretaceous age. Farther south, it places Precambrian gneisses and migmatites against Cretaceous and Jurassic to Triassic rocks. The thrust fault, with an approximate strike of 011.4 ± 8 and dipping to the west, displaces the erosion surface of the Eastern Ranges about 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) vertically according to a topographic survey that was done along the fault. This indicates that the fault has been active. However no displacement of Quaternary deposits were observed during aerial and land reconnaissance work by Page (1986). The slip rate has been estimated at less than 0.2 millimetres (0.0079 in) per year.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]Bibliography
[edit]- Paris, Gabriel; Machette, Michael N.; Dart, Richard L.; Haller, Kathleen M. (2000), Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Folds in Colombia and its Offshore Regions (PDF), USGS, pp. 1–66, retrieved 2017-09-18
- Paris, Gabriel; Machette, Michael N.; Dart, Richard L.; Haller, Kathleen M. (2000), Map of Quaternary Faults and Folds of Colombia and Its Offshore Regions (PDF), USGS, p. 1, retrieved 2017-09-18
Further reading
[edit]- Page, W.D (1986), Seismic geology and seismicity of Northwestern Colombia, San Francisco, California, Woodward-Clyde Consultants Report for ISA and Integral Ltda., Medellín, pp. 1–200