EGL (API)
 | |
| Original author(s) | Khronos Group |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Khronos Group |
| Stable release | 1.5[1]
/ March 19, 2014 |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | API |
| Website | www |
EGL is an interface between Khronos rendering APIs (such as OpenGL, OpenGL ES or OpenVG) and the underlying native platform windowing system. EGL handles graphics context management, surface/buffer binding, rendering synchronization, and enables "high-performance, accelerated, mixed-mode 2D and 3D rendering using other Khronos APIs."[2] EGL is managed by the non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group.
The acronym EGL is an initialism, which starting from EGL version 1.2 refers to Khronos Native Platform Graphics Interface.[3] Prior to version 1.2, the name of the EGL specification was OpenGL ES Native Platform Graphics Interface.[4] X.Org development documentation glossary defines EGL as "Embedded-System Graphics Library".[5]
Adoption
[edit]- The BlackBerry 10 and BlackBerry Tablet OS mobile device operating system uses EGL for 3D graphics rendering. Both support EGL version 1.4.[6]
- The Android mobile device operating system uses EGL for 3D graphics rendering.[7]
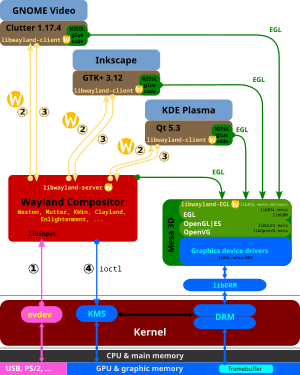
- The Wayland display server protocol uses EGL.[8] It is implemented in a way that Wayland clients will draw directly to the framebuffer using EGL.
- Mesa 3D has an implementation of EGL formerly known as Eagle.[9]
- The Mir display server protocol by Canonical Ltd. uses EGL.[10]
- The Simple DirectMedia Layer toolkit has been ported to use EGL. It can use Xlib, write directly to the framebuffer or use EGL.
- The Raspberry Pi single-board computer has an EGL interface to hardware-accelerated 3D graphics rendering.[11]
- The proprietary Nvidia driver 331.13 BETA from 4 October 2013 supports the EGL API.[12]
- Tizen OS uses EGL with either OpenGL ES 1.1 or OpenGL ES 2.0 for 3D graphics rendering[13]
Implementations
[edit]- Mesa is a free and open-source software implementation of many graphic rendering APIs; among them is EGL.
- Generic Buffer Management is an API to manage buffers.
See also
[edit]- WGL – the equivalent Windows interface to OpenGL
- CGL – the equivalent OS X interface to OpenGL
- GLX – the equivalent X11 interface to OpenGL
- AIGLX – an attempt to accelerate GLX
- WSI – the Vulkan Window System Interface (WSI) does for Vulkan what EGL does for OpenGL ES.
References
[edit]- ^ "Press Release, Khronos Releases EGL 1.5 Specification". Khronos Group. 2014-03-19. Retrieved 2014-03-20.
- ^ "EGL Overview, Native Platform Interface". The Khronos Group. July 19, 2011.
- ^ Jon Leech (ed.). "Khronos Native Platform Graphics Interface (EGL Version 1.2) (July 28, 2005)" (PDF).
- ^ Jon Leech (ed.). "OpenGL® ES Native Platform Graphics Interface (Version 1.0)" (PDF).
- ^ "Glossary". X.Org Foundation.
- ^ "Developer Guide". Archived from the original on 2013-10-10. Retrieved 2014-05-28.
- ^ "Android 2.3 Gingerbread, New Features". Android Developers.
- ^ Pekka Paalanen (10 March 2012). "What does EGL do in the Wayland stack".
- ^ "EGL — The Mesa 3D Graphics Library latest documentation". Mesa 3D Documentation.
- ^ "MirSpec". Archived from the original on 2013-03-06. Retrieved 2013-03-07.
- ^ "Raspberry Pi VideoCore APIs - eLinux.org". elinux.org.
- ^ "Added support for the EGL API on 32-bit platforms. Currently, the supported client APIs are OpenGL ES 1.1, 2.0 and 3.0, and the only supported window system backend is X11". 2013-10-04. Retrieved 2013-10-05.
- ^ "Porting Guide/Graphics and UI - Tizen Wiki". Archived from the original on 2015-04-27. Retrieved 2015-03-06.