Erlenbach–Winkel
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 The site of the prehistoric settlement | |
| Location | Erlenbach, Canton of Zürich, Switzerland |
| Part of | Prehistoric Pile Dwellings around the Alps |
| Criteria | Cultural: (iv), (v) |
| Reference | 1363-050 |
| Inscription | 2011 (35th Session) |
| Area | 3.01 ha (7.4 acres) |
| Buffer zone | 6.6 ha (16 acres) |
| Website | www |
| Coordinates | 47°17′49.93″N 8°35′46.32″E / 47.2972028°N 8.5962000°E |
Erlenbach–Winkel is one of the 111 serial sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps, of which are 56 located in Switzerland.[1][2]
Geography
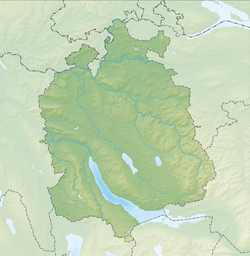
[edit]The site is located on Zürichsee lakeshore in Winkel, a locality of the municipality of Erlenbach in the Canton of Zürich in Switzerland. Because the lake has grown in size over time, the original piles are now around 4 metres (13 ft) to 7 metres (23 ft) under the water level of 406 metres (1,332 ft). The settlement comprises 0.92 hectares (2.27 acres), and the buffer zone including the lake area comprises 49.1 hectares (121.33 acres) in all.
Description
[edit]From the Early Bronze Age (20th/19th centuries BC) numerous finds and ground plans of Corded Ware culture houses are of particular interest. The latter are associated with material from the final phase of the Corded Ware culture marking a hiatus of 600 years until the Early Bronze Age in the period of constructing pile dwellings north of the Alps. In a European context, the house constructions are of particular interest, because the Corded Ware culture is defined mainly by its grave finds, whereas settlements are usually missing from the archaeological records.[3]
Protection
[edit]As well as being part of the 56 Swiss sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps, the settlement is also listed in the Swiss inventory of cultural property of national and regional significance as a Class A object of national importance.[4] Hence, the area is provided as a historical site under federal protection, within the meaning of the Swiss Federal Act on the nature and cultural heritage (German: Bundesgesetz über den Natur- und Heimatschutz NHG) of 1 July 1966. Unauthorised researching and purposeful gathering of findings represent a criminal offense according to Art. 24.[5]
See also
[edit]Literature
[edit]- Peter J. Suter, Helmut Schlichtherle et al.: Pfahlbauten – Palafittes – Palafitte. Palafittes, Biel 2009. ISBN 978-3-906140-84-1.
- Beat Eberschweiler: Ur- und frühgeschichtliche Verkehrswege über den Zürichsee: Erste Ergebnisse aus den Taucharchäologischen Untersuchungen beim Seedamm. In: Mitteilungen des Historischen Vereins des Kantons Schwyz, Volume 96, Schwyz 2004.[6]
References
[edit]- ^ "Prehistoric Pile Dwellings in Switzerland". Swiss Coordination Group UNESCO Palafittes (palafittes.org). Archived from the original on 2014-10-07. Retrieved 2014-12-09.
- ^ "World Heritage". palafittes.org. Archived from the original on 2014-12-09. Retrieved 2014-12-09.
- ^ "Sites Switzerland: Erlenbach–Winkel (CH-ZH-01)". palafittes.org. Archived from the original on 2014-10-07. Retrieved 2014-12-09.
- ^ "A-Objekte KGS-Inventar" (PDF). Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft, Amt für Bevölkerungsschutz. 2015-01-01. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-10-01. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- ^ "Bundesgesetz über den Natur- und Heimatschutz (NHG)" (PDF) (in German). Hochbaudepartement Stadt Zürich. 2014-10-12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-05-15. Retrieved 2015-08-21.
- ^ Beat Eberschweiler (2004). "Ur- und frühgeschichtliche Verkehrswege über den Zürichsee: Erste Ergebnisse aus den Taucharchäologischen Untersuchungen beim Seedamm" (in German). ETH Bibliothek. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2014-12-08.