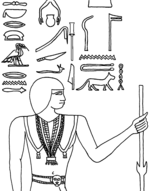
Pehen-Ptah
| Pehen-Ptah in hieroglyphs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Personal name:
Pehen-Ptah pḥn-ptḥ Dedicated to Ptah | ||||||
Honorary title:
Medjeh-qesenw mḏḥ-qsn.w Master of the sculptors | ||||||
 | ||||||
Pehen-Ptah[1] (also read Ptah-Pehen and Ptahpehen[2]) was an ancient Egyptian high official, sculptor and maker of vases[2] during the 2nd Dynasty or early 3rd Dynasty. It is disputed as to who was the king reigning during Pehen-Ptah's time of officeship.
Identity
[edit]Pehen-Ptah is attested by four stone bowl inscriptions only. These were found in the underground storages beneath the Southern Gallery within king Djoser's pyramid necropolis at Saqqara.[2] His name is of some interest to Egyptologists, because it is linked to the god Ptah.[3][4]
Titles
[edit]As a high ranking official and priest, Pehen-Ptah bore several elite and pious titularies:[3]
- God servant of Ptah (Egyptian: hem-netjer ptah).
- Master of the sculptors (Egyptian: Medjehw-qesenw).
- Creator of the (royal) vases (Egyptian: Afet-nebwj).
- Headband of the gods (Egyptian: Shefed-netjerw).
Career
[edit]Next to nothing is known about Pehen-Ptah's career, except for his titles. It is also unknown under which pharaoh he might have served. Since he is mentioned as the "headband of the gods" during a Hebsed, his ruler may have ruled very long, because the Hebsed ("feast of Sed") was commonly celebrated in the 30th year after coronation. There are only two kings from 2nd and 3rd dynasty to have ruled that long: Nynetjer and (possibly) Djoser. It cannot be excluded, however, that Pehen-Ptah served a king who celebrated a Hebsed in advance as is now known to have happened in a few cases, for uncertain reasons. Thus, the problem of determining the exact time period corresponding to Pehen-Ptah's lifetime remains open.[3][4]
References
[edit]- ^ Hermann Ranke: Die ägyptischen Personennamen, Band 1: Verzeichnis der Namen. J. J. Augustin, Glückstadt 1935, p. 139ff.
- ^ a b c Michael Rice: Who is who in Ancient Egypt. Routledge, London/New York 1999. ISBN 978-0-203-44328-6, p.158.
- ^ a b c Pierre Lacau & Jan-Phillip Lauer: La Pyramide à Degrés IV. – Inscriptions gravées sur les Vases: Fouilles à Saqqarah. Service des antiquités de l’Égypte, Cairo 1936, p. 8 & 9.
- ^ a b Aidan Dodson, Dyan Hilton: The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson, London 2004, ISBN 0500051283, p.47.