Portal:Fatimid Caliphate
Portal maintenance status: (January 2019)
|
Introduction
The Fatimid Caliphate (/ˈfætɪmɪd/; Arabic: ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْفَاطِمِيَّة, romanized: al-Khilāfa al-Fāṭimiyya), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shia dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, it ranged from the western Mediterranean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids trace their ancestry to the Islamic prophet Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband Ali, the first Shia imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma'ili communities as well as by denominations in many other Muslim lands and adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids initially conquered Ifriqiya (roughly-present Tunisia and north-eastern Algeria). They extended their rule across the Mediterranean coast and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included—in addition to Egypt—varying areas of the Maghreb, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hejaz.
Between 902 and 909, the foundation of the Fatimid state was realized under the leadership of da'i (missionary) Abu Abdallah, whose conquest of Aghlabid Ifriqiya with the help of Kutama forces paved the way for the establishment of the Caliphate. After the conquest, Abdallah al-Mahdi Billah was retrieved from Sijilmasa and then accepted as the Imam of the movement, becoming the first Caliph and founder of the dynasty in 909. In 921, the city of al-Mahdiyya was established as the capital. In 948, they shifted their capital to al-Mansuriyya, near Kairouan. In 969, during the reign of al-Mu'izz, they conquered Egypt, and in 973, the caliphate was moved to the newly founded Fatimid capital of Cairo. Egypt became the political, cultural, and religious centre of the empire and it developed a new and "indigenous Arabic culture". After its initial conquests, the caliphate often allowed a degree of religious tolerance towards non-Shia sects of Islam, as well as to Jews and Christians. However, its leaders made little headway in persuading the Egyptian population to adopt its religious beliefs. (Full article...)
Selected articles
-
Image 1The Jarrahids (Arabic: بنو الجرَّاح, romanized: Banū al-Jarrāḥ) were an Arab dynasty that intermittently ruled Palestine and controlled Transjordan and northern Arabia in the late 10th and early 11th centuries. They were the ruling family of the Tayy tribe, one of the three powerful tribes of Syria at the time; the other two were Kalb and Kilab.
The Jarrahids first emerged in the Muslim sources as allies of the Qarmatians, and grew prominent under their chieftain Mufarrij ibn Daghfal ibn al-Jarrah. In 973, the latter secured the governorship of Palestine, with Ramla at its center, from the Fatimid Caliphate in reward for military services. Mufarrij lost favor with the Fatimids, who drove the Jarrahids out of Palestine when they plundered Ramla in 981. Afterward, the Jarrahids raided Mecca-bound Hajj pilgrim caravans and vacillated between the Fatimids, Byzantines and individual Muslim rulers in Syria. By 1011–12, the Jarrahids controlled all of interior Palestine up to Tiberias and defied the Fatimids by declaring their own caliph, al-Hasan ibn Ja'far, at Ramla. The Fatimid caliph al-Hakim then paid Mufarrij to end the rebellion, but not long after dispatched an expedition against the Jarrahids in which they were driven from Palestine. (Full article...) -
Image 2Isma'ilism (Arabic: الإسماعيلية, romanized: al-Ismāʿīliyya) is a branch or sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili (/ˌɪzmɑːˈɪliː/) get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (imām) to Ja'far al-Sadiq, wherein they differ from the Twelver Shia, who accept Musa al-Kazim, the younger brother of Isma'il, as the true Imām.
After the death of Muhammad ibn Isma'il in the 8th century CE, the teachings of Ismailism further transformed into the belief system as it is known today, with an explicit concentration on the deeper, esoteric meaning (batin) of the Islamic religion. With the eventual development of Usulism and Akhbarism into the more literalistic (zahir) oriented, Shia Islam developed into two separate directions: the metaphorical Ismaili, Alevi, Bektashi, Alian, and Alawite groups focusing on the mystical path and nature of God, along with the "Imam of the Time" representing the manifestation of esoteric truth and intelligible divine reality, with the more literalistic Usuli and Akhbari groups focusing on divine law (sharia) and the deeds and sayings (sunnah) of Muhammad and the Twelve Imams who were guides and a light to God. (Full article...) -
Image 3El-Mansuriya or Mansuriya (Arabic: المنصورية), also known as Sabra or Sabra al-Mansuriyya, near Kairouan, Tunisia, was the capital of the Fatimid Caliphate during the rule of the Ismaili Imams al-Mansur bi-Nasr Allah (r. 946–953) and al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah (r. 953–975).
Built between 946 and 972, el-Mansuriya was a walled city holding elaborate palaces surrounded by gardens, artificial pools and water channels. It was briefly the centre of a powerful state that encompassed most of North Africa and Sicily. It continued to serve as provincial capital of the Zirids until 1057, when it was destroyed by the invading Banu Hilal tribes. Any useful objects or relics were scavenged during the centuries that followed. Today, only faint traces remain. (Full article...) -
Image 4Abū al-Qāsim Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh (Arabic: أبو القاسم محمد ابن عبد الله; March/April 893 – 17 May 946), better known by his regnal name al-Qāʾim (القائم) or al-Qāʾim bi-Amr Allāh (Arabic: القائم بأمر الله, lit. 'He who carries out God's orders'), was the second caliph of the Fatimid dynasty, ruling in Ifriqiya from 934 to 946. He was the twelfth Isma'ili Imam, succeeding his father Abd Allah al-Mahdi Billah (r. 909–934). (Full article...)
-
Image 5Shawar ibn Mujir al-Sa'di (Arabic: شاور بن مجير السعدي, romanized: Shāwar ibn Mujīr al-Saʿdī; died 18 January 1169) was an Arab de facto ruler of Fatimid Egypt, as its vizier, from December 1162 until his assassination in 1169 by the general Shirkuh, the uncle of the future Ayyubid leader Saladin, with whom he was engaged in a three-way power struggle against the Crusader Amalric I of Jerusalem. Shawar was notorious for continually switching alliances, allying first with one side, and then the other, and even ordering the burning of his own capital city, Fustat, just so that the enemy could not have it. (Full article...)
-
Image 6Asad ad-Dīn Shīrkūh bin Shādhī (Kurdish: ئەسەدەدین شێرکۆ, romanized: Esed El-Dîn Şêrko; Arabic: أسد الدين شيركوه بن شاذي), also known as Shirkuh, or Şêrko (meaning "lion of the mountains" in Kurdish) (died 23 March 1169) was a Kurdish Mercenary commander in service of the Zengid dynasty, then the Fatimid Caliphate and uncle of Saladin. His military and diplomatic efforts in Egypt were a key factor in establishing the Ayyubid dynasty in that country. (Full article...)
-
Image 7The Sulayhid dynasty (Arabic: بَنُو صُلَيْح, romanized: Banū Ṣulayḥ, lit. 'Children of Sulayh') was an Ismaili Shi'ite Arab dynasty established in 1047 by Ali ibn Muhammad al-Sulayhi that ruled most of historical Yemen at its peak. The Sulayhids brought to Yemen peace and a prosperity unknown since Himyaritic times. The regime was confederate with the Cairo-based Fatimid Caliphate, and was a constant enemy of the Rassids - the Zaidi Shi'ite rulers of Yemen throughout its existence. The dynasty ended with Arwa al-Sulayhi affiliating to the Taiyabi Ismaili sect, as opposed to the Hafizi Ismaili sect that the other Ismaili dynasties such as the Zurayids and the Hamdanids adhered to. (Full article...)
-
Image 8Abu'l Muzaffar Bahram al-Armani al-Hafizi (Arabic: بهرام) was the vizier of the Fatimid Caliphate in 1135–1137, under the Caliph al-Hafiz li-Din Allah. (Full article...)
-
Image 9Abu'l-Faraj Ya'qub ibn Yusuf ibn Killis (Arabic: يعقوب ابن كلس, romanized: Abu’l-Faraj Yaʿqūb ibn Yūsuf ibn Killis, Hebrew: יעקוב אבן כיליס), (c. 930 in Baghdad – 991), commonly known simply by his patronymic surname as Ibn Killis, was a high-ranking official of the Ikhshidids who went on to serve as vizier under the Fatimids from 979 until his death in 991.
Ya'qub ibn Yusuf ibn Killis was born in Baghdad in about 930 in a Jewish family. After his family moved to Syria he came to Egypt in 943 and entered the service of the Regent Kafur. As soon as he became the household and property administrator, he was in charge of the Egyptian state's finances. Despite converting to Islam in 967, he was imprisoned by Kafur's successors after losing their favor. He was able however to purchase his freedom and went to Ifriqiya, where he put himself at the service of the Fatimid Caliph al-Mu'izz. (Full article...) -
Image 10The navy of the Fatimid Caliphate was one of the most developed early Muslim navies and a major force in the central and eastern Mediterranean in the 10th–12th centuries. As with the dynasty it served, its history is in two phases. The first was c. 909 to 969, when the Fatimids were based in Ifriqiya (modern Tunisia); the second lasted until the end of the dynasty in 1171, when they were based in Egypt. During the first period, the navy was employed mainly against the Byzantine Empire in Sicily and southern Italy, where it enjoyed mixed success. It was also in the initially unsuccessful attempts to conquer Egypt from the Abbasids and brief clashes with the Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba.
During the first decades after the eventual Fatimid conquest of Egypt in 969, the main naval enemy remained the Byzantines, but the war was fought mostly on land over control of Syria, and naval operations were limited to maintaining Fatimid control over the coastal cities of the Levant. Warfare with the Byzantines ended after 1000 with a series of truces, and the navy became once more important with the arrival of the Crusaders in the Holy Land in the late 1090s. (Full article...) -
Image 11The second Fatimid invasion of Egypt occurred in 919–921, following the failure of the first attempt in 914–915. The expedition was again commanded by the Fatimid Caliphate's heir-apparent, al-Qa'im bi-Amr Allah. As during the previous attempt, the Fatimids captured Alexandria with ease. However, while the Abbasid garrison in Fustat was weaker and mutinous due to lack of pay, al-Qa'im did not exploit it for an immediate attack on the city, such as the one that had failed in 914. Instead, in March 920, the Fatimid navy was destroyed by the Abbasid fleet under Thamal al-Dulafi, and Abbasid reinforcements under Mu'nis al-Muzaffar arrived at Fustat. Nevertheless, in the summer of 920, al-Qa'im was able to capture the Fayyum Oasis, and in the spring of 921, extend his control over much of Upper Egypt as well, while Mu'nis avoided an open confrontation and remained at Fustat. During that time, both sides were engaged in a diplomatic and propaganda battle, with the Fatimids' in particular trying to sway the Muslim populace to their side, without success. The Fatimid expedition was condemned to failure when Thamal's fleet took Alexandria in May/June 921; when the Abbasid forces moved on Fayyum, al-Qa'im was forced to abandon it and flee west over the desert. (Full article...)
-
Image 12Abū'l-Futūh Barjawān al-Ustādh (عَبْدُ الْفُتُوحِ بَرْجَوَانِ الْأُسْتَاذِ; died 25/26 March 1000) was a eunuch palace official who became the prime minister (wāsiṭa) and de facto regent of the Shia Fatimid Caliphate in October 997, and held the position until his assassination. Of obscure origin, Barjawan became the tutor of heir-apparent al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah, who became caliph in 996 with the death of al-Aziz Billah. On al-Hakim's coronation, power was seized by the Kutama Berbers, who tried to monopolize government and clashed with their rivals, the Turkic slave-soldiers. Allied with disaffected Berber leaders, Barjawan was able to seize the reins of government for himself in 997. His tenure was marked by a successful balancing act between the Berbers and the Turks, as well as the rise of men of diverse backgrounds, promoted under his patronage. Militarily, Barjawan was successful in restoring order to the Fatimids' restive Levantine and Libyan provinces, and set the stage for an enduring truce with the Byzantine Empire. The concentration of power in his hands and his overbearing attitude alienated al-Hakim, however, who ordered him assassinated and thereafter assumed the governance of the caliphate himself. (Full article...)
-
Image 13Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥasan al-Aʿsam ibn Aḥmad ibn al-Ḥasan ibn Bahrām al-Jannābī (Arabic: أَبُو عَلِيّ ٱلحَسَن ٱلأَعْصَم بْنُ أَحْمَد بْنِ ٱلحَسَن بْنِ بَهْرَام الجَنَّابِيّ; al-Ahsa Oasis, 891 – Ramla, 977), was a Qarmatian leader, chiefly known as the military commander of the Qarmatian invasions of Syria (especially around Damascus and Palestine) in 968–977. Already in 968, he led attacks on the Ikhshidids, capturing Damascus and Ramla and extracting pledges of tribute. Following the Fatimid conquest of Egypt and the overthrow of the Ikhshidids, in 971–974 al-A'sam led attacks against the Fatimid Caliphate, who began to expand into Syria. The Qarmatians repeatedly evicted the Fatimids from Syria and invaded Egypt itself twice, in 971 and 974, before being defeated at the gates of Cairo and driven back. Al-A'sam continued fighting against the Fatimids, now alongside the Turkish general Alptakin, until his death in March 977. In the next year, the Fatimids managed to overcome the allies, and concluded a treaty with the Qarmatians that signalled the end of their invasions of Syria. (Full article...)
-
Image 14Tala'i ibn Ruzzik (Arabic: طلائع ﺑﻦ ﺭﺯﻳﻚ, romanized: Ṭalāʾīʿ ibn Ruzzīk, with his full titles and surnames Abū'l-Gharāt Fāris al-Muslimīn al-Malik al-Ṣāliḥ Ṭalāʾīʿ ibn Ruzzīk al-Ghassānī al-Armanī) was a military commander and official of the Fatimid Caliphate, serving as its vizier from 1154 until his assassination in 1161, when he was succeeded by his son, Ruzzik ibn Tala'i. He is generally acknowledged as the last of the powerful and capable viziers of the Fatimid state. During his tenure the Fatimid Caliphate regained a measure of stability, and was once again able to project its power abroad and pursue its political interests in the Eastern Mediterranean. (Full article...)
-
Image 15Abu'l-Ashbāl al-Ḍirghām ibn ʿĀmir ibn Sawwār al-Lukhamī (Arabic: أبو الأشبال ضرغام بن عامر بن سوار اللخمي) (fl. 1153–1164) was an Arab military commander in the service of the Fatimid Caliphate. An excellent warrior and model cavalier, he rose to higher command and scored some successes against the Kingdom of Jerusalem as well as against internal rebellions. Despite his close personal ties to the viziers Tala'i ibn Ruzzik and his son Ruzzik ibn Tala'i, he joined Shawar when the latter rebelled against Ruzzik and seized the vizierate. Nine months later, Dirgham betrayed Shawar as well and expelled him from the capital, becoming vizier himself on 31 August 1163. Amidst yet another Crusader invasion in 1164, Dirgham clashed with Shawar, who had gained the support of Syrian troops led by Shirkuh. Deserted by most of his troops, Dirgham was killed sometime in May–August 1164 by Shawar's army. (Full article...)
-
Image 16Abu'l-Najm Badr ibn Abdallah al-Jamali al-Mustansiri, better known as Badr al-Jamali (Arabic: بدر الجمالى) or by his eventual title as Amir al-Juyush (أمير الجيوش, lit. 'Commander of the Armies'), was a military commander and statesman for the Fatimid Caliphate under Caliph al-Mustansir. Of Armenian origin but a convert to Islam, Badr had been brought up as a military slave (mamluk) by the ruler of Tripoli, Jamal al-Dawla ibn Ammar. In the 1060s, he was appointed twice as governor of Damascus in Syria, at a time when Fatimid authority there was disintegrating, and the central government in Egypt was on the verge of collapse as a result of the Mustansirite Hardship. Badr was unable to prevent the loss of most of Syria to local potentates and Turkoman warlords, but managed to hold on to the coastal cities, making Acre his base.
As the sole major military commander outside Egypt, he was called upon by al-Mustansir to help rescue the dynasty. Badr landed in Egypt in late 1073, rapidly eliminated his rivals, and was appointed vizier with plenipotentiary powers, making him a quasi-sultan or military dictator, with the caliph relegated to his religious duties as Isma'ili imam. Control over the state was solidified with the marriage of one of his daughters to al-Mustansir, and the appointment of his own son, al-Afdal Shahanshah, as his successor in 1085. Badr managed to restore order in Egypt and initiated major administrative reforms, defeated Turkoman attempts to invade Egypt, and recovered control over Palestine and the Hejaz. He initiated a series of new constructions, including the Juyushi Mosque and the new city wall of Cairo, some of whose gates stand to this day. Badr's renure saved the Fatimid regime, but also began a period where the vizierate was dominated by military strongmen who held power on their own, rather than through caliphal appointment, and who increasingly sidelined the caliphs to puppet rulers. Badr also initiated a wave of Armenian migration into Egypt, and was the first of a series of viziers of Armenian origin, who played a major role in the fortunes of the Fatimid Caliphate over the subsequent century. (Full article...) -
Image 17The Fatimid architecture that developed in the Fatimid Caliphate (909–1167 CE) of North Africa combined elements of eastern and western architecture, drawing on Abbasid architecture, Byzantine, Ancient Egyptian, Coptic architecture and North African traditions; it bridged early Islamic styles and the medieval architecture of the Mamluks of Egypt, introducing many innovations.
The wealth of Fatimid architecture was found in the main cities of Mahdia (921–948), Al-Mansuriya (948–973) and Cairo (973–1169). The heartland of architectural activity and expression during Fatimid rule was at al-Qahira (Cairo), on the eastern side of the Nile, where many of the palaces, mosques and other buildings were built. Large-scale constructions were undertaken during the reigns of al-Mui'zz (r. 953–975) Al-Aziz Billah (r. 975–996) and al-Hakim (r. 996–1021). (Full article...) -
Image 18Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn Yūsuf ibn al-Ḥāfiẓ (Arabic: أبو محمد عبد الله بن يوسف بن الحافظ; 1151–1171), better known by his regnal name al-ʿĀḍid li-Dīn Allāh (Arabic: العاضد لدين الله, lit. 'Strengthener of God's Faith'), was the fourteenth and last caliph of the Fatimid dynasty, and the twenty-fourth imam of the Hafizi Isma'ili branch of Shi'a Islam, reigning from 1160 to 1171.
Like his two immediate predecessors, al-Adid came to the throne as a child, and spent his reign as a puppet of various strongmen who occupied the vizierate. He was a mostly helpless bystander to the slow collapse of the Fatimid Caliphate. Tala'i ibn Ruzzik, the vizier who had raised al-Adid to the throne, fell victim to a palace plot in 1161, and was replaced by his son, Ruzzik ibn Tala'i. Ruzzik was in turn overthrown by Shawar in 1163, but the latter lasted only a few months in office before being overthrown by Dirgham. The constant power struggles in Cairo enfeebled the Fatimid state, allowing both the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Sunni ruler of Syria, Nur al-Din, to advance their own designs on the country. The Crusaders repeatedly invaded Egypt, extracting tribute and ultimately aiming to conquer it; in turn, Nur al-Din supported Shawar's bid to retake the vizierate from Dirgham, and sent his general Shirkuh to counter the Crusaders. For a while, Shawar played the Crusaders and Syrians against one another, but in January 1169, Shirkuh overthrew Shawar, occupied Cairo and became vizier. When Shirkuh died shortly after, he was succeeded by his nephew, Saladin. (Full article...) -
Image 19Abu Ali al-Mansur ibn al-Musta'li (Arabic: أبو علي المنصور بن المستعلي, romanized: Abū ʿAlī al-Manṣūr ibn al-Mustaʿlī; 31 December 1096 – 7 October 1130), better known by his regnal name al-Amir bi-Ahkam Allah (Arabic: الآمر بأحكام الله, romanized: al-Āmir bi-Aḥkām Allāh, lit. 'The Ruler Who Executes God's Decrees') was the tenth Fatimid caliph, ruling from 1101 to his death in 1130, and the 20th imam of the Musta'li Isma'ili branch of Shia Islam.
Al-Amir succeeded his father, al-Musta'li, at the age of five. For the first twenty years of his reign, al-Amir was a puppet of his uncle and father-in-law, the vizier al-Afdal Shahanshah, who ruled the Fatimid state and confined al-Amir, like al-Musta'li before him, to the palace. In December 1121, al-Afdal was murdered, officially by agents of the rival Nizari branch of Isma'ilism, although some medieval accounts blame al-Amir and al-Afdal's chief secretary, al-Ma'mun al-Bata'ihi, instead. Al-Amir and al-Bata'ihi moved quickly to forestall a succession by one of al-Afdal's sons, imprisoning them and moving the vast treasures al-Afdal had amassed into the caliphal palace. Al-Bata'ihi was appointed as the new vizier, but al-Amir took an increasing role in government, and was prominently featured in spectacular public ceremonies. Finally, in 1125, al-Amir dismissed and imprisoned al-Bata'ihi, ruling thenceforth without a vizier. (Full article...) -
Image 20Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-Ḥusayn (Arabic: أبو محمد عبد الله بن الحسين; 31 July 874 – 4 March 934), better known by his regnal name al-Mahdī biʾllāh (Arabic: المهدي بالله, "The Rightly Guided by God"), was the founder of the Isma'ili Fatimid Caliphate, the only major Shi'a caliphate in Islamic history, and the eleventh Imam of the Isma'ili branch of Shi'ism.
He was born as Saʿīd ibn al-Ḥusayn (سعيد بن الحسين) in Askar Mukram to a family that led the secret Isma'ili missionary network (da'wa), propagating on behalf of the hidden imam, Muhammad ibn Isma'il, who would return as the prophesied Islamic messiah (mahdi). Orphaned at a young age, he moved to Salamiya, the family's base of operations, where he was adopted by his uncle. In the mid-890s Sa'id succeeded to the leadership of the expanding da'wa, which had expanded and gained adherents across the then Muslim world. However, his claims of not merely being a trustee of the hidden imam, but of him and his ancestors holding the imamate itself, led in 899 to a schism in the Isma'ili movement: those who did not recognize his claims split off to become the Qarmatians. The schism was followed by uprisings of pro-Isma'ili Bedouin in Syria in 902–903, launched without his consent by over-eager supporters, who aimed to force him to come forward as the mahdi. The Bedouin uprising was suppressed by the Abbasids, but drew the attention of the Abbasid Caliphate's authorities to him, forcing him to abandon Salamiya, and flee first to Ramla, then Fustat in Egypt, and finally Sijilmasa in what is now Morocco. There he remained, living as a merchant, until one of his missionaries, Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i, at the head of the Kutama Berbers overthrew the Aghlabid dynasty of Ifriqiya in 909. (Full article...) -
Image 21Al-Amīr al-Mukhtār ʿIzz al-Mulk Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Abīʾl Qāsim ʿUbayd Allāh ibn Aḥmad ibn Ismāʿīl ibn ʿAbd al-Azīz al-Ḥarranī al-Musabbiḥī al-Kātib, commonly known simply as al-Musabbihi (Arabic: المصبحي) (4 March 977 – April/May 1030), was a Sunni Fatimid historian, writer and administrative official. He is known to have authored some 40,000 pages of manuscripts dealing with an array of topics, including history, psychology, law, grammar, sexology and cooking. Akhbār Miṣr, a contemporary chronicle of Egyptian history and news, was among al-Musabbihi's well-known works. However, like the vast majority of al-Musabbihi's works, only fragments of Akhbār Miṣr survived; most of his writings disappeared not long after his death.
Al-Musabbihi was a devout Sunni Muslim born in Fustat, where he lived most of his life and died. He was known to be loyal to the Fatimid government and he was a close friend of with Caliph al-Hakim (r. 996–1021). Early in his career, he served in the Fatimid military and was made a provincial governor in Upper Egypt before becoming a leading figure in the Fatimids' central administration in Cairo. (Full article...) -
Image 22Abū al-Ḥasan ʿAlī ibn al-Ḥākim (Arabic: أبو الحسن علي ابن الحاكم; 20 June 1005 – 13 June 1036), better known with his regnal name al-Ẓāhir li-Iʿzāz Dīn Allāh (Arabic: الظاهر لإعزاز دين الله, lit. 'He Who Appears Openly to Strengthen the Religion of God'), was the seventh caliph of the Fatimid dynasty (1021–1036). Al-Zahir assumed the caliphate after the disappearance of his father al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah. (Full article...)
-
Image 23Nizari Isma'ilism (Arabic: النزارية, romanized: al-Nizāriyya) are the largest segment of the Ismaili Muslims, who are the second-largest branch of Shia Islam after the Twelvers. Nizari teachings emphasize independent reasoning or ijtihad; pluralism—the acceptance of racial, ethnic, cultural and inter-religious differences; and social justice. Nizaris, along with Twelvers, adhere to the Jaʽfari school of jurisprudence. The Aga Khan, currently Aga Khan IV, is the spiritual leader and Imam of the Nizaris. The global seat of the Ismaili Imamate is in Lisbon, Portugal. (Full article...)
-
Image 24Cairo (/ˈkaɪroʊ/ ⓘ KY-roh; Arabic: القاهرة, romanized: al-Qāhirah, Egyptian Arabic pronunciation: [el.qɑ(ː)ˈheɾɑ] ⓘ) is the capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East. The Greater Cairo metropolitan area is the 12th-largest in the world by population with over 22.1 million people.
Cairo is associated with ancient Egypt, as the Giza pyramid complex and the ancient cities of Memphis and Heliopolis are located in its geographical area. Located near the Nile Delta, the city first developed as Fustat following the Muslim conquest of Egypt in 641 next to an existing ancient Roman fortress, Babylon. Cairo was founded by the Fatimid dynasty in 969. It later superseded Fustat as the main urban centre during the Ayyubid and Mamluk periods (12th–16th centuries). Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life, and is titled "the city of a thousand minarets" for its preponderance of Islamic architecture. Cairo's historic center was awarded World Heritage Site status in 1979. Cairo is considered a World City with a "Beta +" classification according to GaWC. (Full article...) -
Image 25Najm al-Dīn Umāra al-Ḥakamī al-Yamanī (Arabic: نجم الدين عمارة الحكمي اليمني) was a Sunni historian, jurist and poet of Yemen of great repute who was closely associated with the late Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. He was executed by order of Saladin at Cairo on April 6, 1174 for his part in a conspiracy to restore Fatimid rule. His Tarikh al-Yaman is the earliest, and in respects the most important, history of Yemen from the Islamic era. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that the last Fatimid caliph, al-Adid, came to the throne as a child, was dominated by his viziers, and died a few days after Saladin abolished the Fatimid regime?
- ... that in the judgment of historians, the Fatimid caliph al-Musta'li "had no noteworthy life", as he was a puppet of his vizier, al-Afdal?
- ... that Da'ud, the heir apparent of the last Fatimid caliph, spent almost his entire life imprisoned by the succeeding Ayyubid dynasty?
- ... that medieval Muslim historians blamed al-Amir bi-Ahkam Allah for the loss of much of Palestine to the crusaders but, in reality, he played no role in the Fatimid government during that period?
Need help?
Do you have a question about the Fatimid Caliphate that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk or at the talk page of WikiProject Islam.
If you are interested in reading more about the Fatimid caliphate, some up-to-date summary books and encyclopedia articles are:
- Brett, Michael (2017). The Fatimid Empire. The Edinburgh History of the Islamic Empires. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0-7486-4076-8.
- Daftary, Farhad (1999). "Fatimids". In Yarshater, Ehsan (ed.). Encyclopædia Iranica, Volume IX/4: Fārs II–Fauna III. London and New York: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 423–426. ISBN 978-0-933273-32-0.
- Halm, Heinz (2014). "Fāṭimids". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam (3rd ed.). Brill Online. ISSN 1873-9830.
- Sanders, Paula (1998). "The Fāṭimid state, 969–1171". In Petry, Carl F. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Egypt, Volume 1: Islamic Egypt, 640–1517. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 151–174. ISBN 0-521-47137-0.
- Walker, Paul E. (1998). "The Ismā'īlī Da'wa and the Fātimid caliphate". In Petry, Carl F. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Egypt, Volume 1: Islamic Egypt, 640–1517. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 120–150. ISBN 0-521-47137-0.
- Walker, Paul E. (2018). "Fāṭimids". In Madelung, Wilferd; Daftary, Farhad (eds.). Encyclopaedia Islamica Online. Brill Online. ISSN 1875-9831.
Selected images
-
Image 1Fatimid Caliph al-Mahdi Billah receiving an envoy from Simeon I of Bulgaria, Madrid Skylitzes, 12th century. (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 3Image of two standing soldiers. 11th century, Fatimid period, from Fustat near Cairo. Museum of Islamic Art, Cairo, inv. no. 13703. Attribution to the Fatimid period is sometimes questioned. (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 4Fatimid ewer, 10th century CE (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 5Bab al-Futuh, one of the gates of Cairo dating from Badr al-Jamali's reconstruction of the city walls (1987) (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 6The Al-Hakim Mosque in Cairo, commissioned by al-Aziz in 990 and completed by al-Hakim in 1013 (later renovated in the 1980s by the Dawoodi Bohra) (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 7Cover page of the Leningrad Codex, a manuscript of the Hebrew Bible copied in Cairo/Fustat in the early 11th century (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 8Men hunting, on ivory panel, 11th century (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 9Al-Salih Tala'i Mosque in Cairo, built by Tala'i ibn Ruzzik in 1160 and originally intended to house the head of Husayn (the head ended up being interred instead at the present-day al-Hussein Mosque) (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 10Lustreware Plate with Bird Motif, 11th century. Archaeological digs have found many kilns and ceramic fragments in al-Fustat, and it was likely an important production location for Islamic ceramics during the Fatimid period. (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 11Side chapel in the Hanging Church in Old Cairo, including frescoes (partly visible behind the screen here) dating from the late 12th or 13th century, before the church's later renovation (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 12Architectural fragment from a bathhouse in al-Fustat, 11th century CE (pre-1168 CE). Museum of Islamic Art, Cairo, 12880. (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
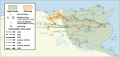
Image 13Map of Abu Abdallah's campaigns and battles during the overthrow of the Aghlabids (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 14Fatimid gold dinar minted during the reign of al-Mustansir Billah (1036–1094) (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 16Fragments of mosaic pavement from the palace of al-Qa'im in al-Mahdiyya (Mahdia), on display at the Mahdia Museum (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 17Al-Juyushi Mosque, Cairo, overlooking the city from the Muqattam Hills (from Fatimid Caliphate)
-
Image 18Al-Azhar Mosque in Cairo, built by the Fatimids between 970 and 972 (from Fatimid Caliphate)
Subcategories
Subtopics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus