Mars habitability analogue environments on Earth
Mars habitability analogue environments on Earth are environments that share potentially relevant astrobiological conditions with Mars. These include sites that are analogues of potential subsurface habitats, and deep subsurface habitats.[1]
A few places on Earth, such as the hyper-arid core of the high Atacama Desert and the McMurdo Dry Valleys in Antarctica approach the dryness of current Mars surface conditions. In some parts of Antarctica, the only water available is in films of brine on salt / ice interfaces. There is life there, but it is rare, in low numbers, and often hidden below the surface of rocks (endoliths), making the life hard to detect. Indeed, these sites are used for testing sensitivity of future life detection instruments for Mars, furthering the study of astrobiology, for instance, as a location to test microbes for their ability to survive on Mars, and as a way to study how Earth life copes in conditions that resemble conditions on Mars.
Other analogues duplicate some of the conditions that may occur in particular locations on Mars. These include ice caves, the icy fumaroles of Mount Erebus, hot springs, or the sulfur rich mineral deposits of the Rio Tinto region in Spain. Other analogues include regions of deep permafrost and high alpine regions with plants and microbes adapted to aridity, cold and UV radiation with similarities to Mars conditions.[1][2]
Precision of analogues
[edit]Mars surface conditions are not reproduced anywhere on Earth, so Earth surface analogues for Mars are necessarily partial analogues. Laboratory simulations show that whenever multiple lethal factors are combined, the survival rates plummet quickly.[3] There are no full-Mars simulations published yet that include all of the biocidal factors combined.[3]
- Ionizing radiation. Curiosity rover measured levels on Mars similar to the interior of the International Space Station (ISS), which is far higher than surface Earth levels.[4][5]
- Atmosphere. The Martian atmosphere is a near vacuum while Earth's is not. Through desiccation resistance, some life forms can withstand the vacuum of space in dormant state.[5][6][7][8][9]
- UV levels. UV levels on Mars are much higher than on Earth. Experiments show that a thin layer of dust is enough to protect microorganisms from UV radiation.[6]
- Oxidizing surface. Mars has a surface layer which is highly oxidizing (toxic) because it contains salts such as perchlorates, chlorates, cholorites, and sulfates pervasive in the soil and dust,[10][11] and hydrogen peroxide throughout the atmosphere.[12] Earth does have some areas that are highly oxidizing, such as the soda lakes, and though not direct analogues, they have conditions that may be duplicated in thin films of brines on Mars.
- Temperature. Nowhere on Earth reproduces the extreme changes in temperature that happen within a single day on Mars.
- Dry ice. The Mars surface consists of dry ice (CO2 ice) in many areas. Even in equatorial regions, dry ice mixed with water forms frosts for about 100 days of the year. On Earth, although temperatures on Earth briefly get cold enough for dry ice to form in the Antarctic interior at high altitudes, the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere is too low for dry ice to form because the depositional temperature for dry ice on Earth under 1 bar of pressure is −140 °C (−220 °F)[13] and the lowest temperature recorded in Antarctica is −94.7 °C (−138.5 °F), recorded in 2010 by satellite.[14]
These partial analogues are useful, for instance for:[2]
- Testing life detection equipment which may one day be sent to Mars
- Studying conditions for preservation of past life on Mars (biosignatures)
- Studying adaptations to conditions similar to those that may occur on Mars
- As a source of microbes, lichens etc. that can be studied as they may exhibit resistance to some conditions present on Mars.
Atacama Desert
[edit]The Atacama Desert plateau lies at an altitude of 3,000 meters and lies between the Pacific and the Andes mountains. Its Mars-like features include
- Hyper arid conditions
- Cold compared to most arid deserts because of the altitude
- High levels of UV light (because it is relatively cloudless, also the higher altitude means less air to filter the UV out, and the ozone layer is somewhat thinner above sites in the southern hemisphere than above corresponding sites in the northern hemisphere[15][16])
- Salt basins, which also include perchlorates making them the closest analogues to Martian salts on Earth.[1]
Yungay area
[edit]The Yungay area at the core of the Atacama Desert used to be considered the driest area on Earth for more than a decade, until the discovery in 2015 that Maria Elena South is drier.[17][18] It can go centuries without rainfall, and parts of it have been hyper-arid for 150 million years. The older regions in this area have salts that are amongst the closest analogues of salts on Mars because these regions have nitrate deposits that contain not only the usual chlorides, but also sulfates, chlorates, chromates, iodates, and perchlorates.[19] The infrared spectra are similar to the spectra of bright soil regions of Mars.[1]
The Yungay area has been used for testing instruments intended for future life detection missions on Mars, such as the Sample Analysis at Mars instruments for Curiosity, the Mars Organic Analyzer for ExoMars, and Solid3 for Icebreaker Life, which in 2011, in a test of its capabilities, was able to find a new "microbial oasis" for life two meters below the surface of the Atacama desert.[19][20][21] It is the current testing site for the Atacama Rover Astrobiology Drilling Studies (ARADS) project to improve technology and strategies for life detection on Mars.[22][23]
Experiments conducted on Mars have also been successfully repeated in this region. In 2003, a group led by Chris McKay repeated the Viking Lander experiments in this region and got the same results as those of the Viking landers on Mars: decomposition of the organics by non-biological processes. The samples had trace elements of organics, no DNA was recovered, and extremely low levels of culturable bacteria.[24] This led to increased interest in the site as a Mars analogue.[25]
Although hardly any life, including plant or animal life, exists in this area,[1] the Yungay area does have some microbial life, including cyanobacteria, both in salt pillars, as a green layer below the surface of rocks, and beneath translucent rocks such as quartz.[25][26][27] The cyanobacteria in the salt pillars have the ability to take advantage of the moisture in the air at low relative humidities. They begin to photosynthesize when the relative humidity rises above the deliquescence relative humidity of salt, at 75%, presumably making use of deliquescence of the salts.[26] Researchers have also found that cyanobacteria in these salt pillars can photosynthesize when the external relative humidity is well below this level, taking advantage of micropores in the salt pillars which raise the internal relative humidity above the external levels.[28] [29]
Maria Elena South
[edit]This site is even drier than the Yungay area. It was found through a systematic search for drier regions than Yungay in the Atacama Desert, using relative humidity data loggers set up from 2008 to 2012, with the results published in 2015.[17] The relative humidity is the same as the lowest relative humidity measured by Curiosity rover.[18]
A 2015 paper reported [17] an average atmospheric relative humidity 17.3%, and soils relative humidity a constant 14% at depth of 1 meter, which corresponds to the lowest humidity measured by Curiosity rover on Mars. This region's maximum atmospheric relative humidity is 54.7% compared with 86.8% for the Yungay region.
The following living organisms were also found in this region:
- Actinomycetota: Actinobacterium, Aciditerrmonas, and Geodermatophilus
- Pseudomonadota: Caulobacter and Sphingomonas
- Bacillota: Clostridiales
- Acidobacteriota: Acidobacterium
- 16 new species of Streptomyces, 5 of Bacillus and 1 of Geodermatophilus.
There was no decrease in the numbers of species as the soil depth increased down to a depth of one meter, although different microbes inhabited different soil depths. There was no colonization of gypsum, showing the extreme dryness of the site.
No archaea was detected in this region using the same methods that detected archaea in other regions of the Atacama Desert. The researchers said that if this is confirmed in studies of similarly dry sites, it could mean that "there may be a dry limit for this domain of life on Earth."[17]
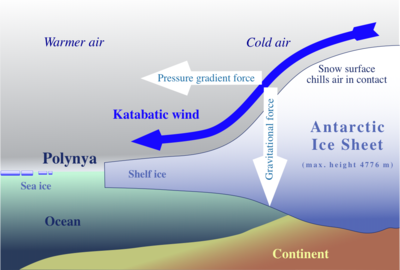
McMurdo Dry Valleys in Antarctica
[edit]
These valleys lie on the edge of the Antarctic plateau. They are kept clear of ice and snow by fast katabatic winds that blow from the plateau down through the valleys. As a result, they are amongst the coldest and driest areas in the world.
The central region of Beacon Valley is considered to be one of the best terrestrial analogues for the current conditions on Mars. There is snowdrift and limited melting around the edges and occasionally in the central region, but for the most part, moisture is only found as thin films of brine around permafrost structures. It has slightly alkaline salt rich soil.[30][31]
Don Juan Pond
[edit]Don Juan Pond is a small pond in Antarctica, 100 meters by 300 meters, and 10 cm deep, that is of great interest for studying the limits of habitability in general. Research using a time-lapse camera shows that it is partly fed by deliquescing salts. The salts absorb water by deliquescence only, at times of high humidity, then flows down the slope as salty brines. These then mix with snow melt, which feeds the lake. The first part of this process may be related to the processes that form the Recurring Slope Lineae (RSLs) on Mars.[32][33]
This valley has an exceptionally low water activity (aw) of 0.3 to 0.6. Though microbes have been retrieved from it, they have not been shown to be able to reproduce in the salty conditions present in the lake, and it is possible that they only got there through being washed in by the rare occasions of snow melt feeding the lake.
Blood Falls
[edit]
This unusual flow of melt water from below the glacier gives scientists access to an environment they could otherwise only explore by drilling (which would also risk contaminating it). The melt water source is a subglacial pool of unknown size which sometimes overflows. Biogeochemical analysis shows that the water is marine in source originally. One hypothesis is that the source may be the remains of an ancient fjord that occupied the Taylor valley in the tertiary period. The ferrous iron dissolved in the water oxidizes as the water reaches the surface, turning the water red.[34]
Its autotrophic bacteria metabolize sulfate and ferric ions.[35][36] According to geomicrobiologist Jill Mikucki at the University of Tennessee, water samples from Blood Falls contained at least 17 different types of microbes and almost no oxygen.[35] An explanation may be that the microbes use sulfate as a catalyst to respire with ferric ions and metabolize the trace levels of organic matter trapped with them. Such a metabolic process had never before been observed in nature.[35] This process is of astrobiological importance as an analogue for environments below the Glaciers on Mars, if there is any liquid water there, for instance through hydrothermal melting (though none such has been discovered yet).[37][38] This process is also an analogue for cryovolcanism in icy moons such as Enceladus.
Subglacial environments in Antarctica need similar protection protocols to interplanetary missions.
"7. Exploration protocols should also assume that the subglacial aquatic environments contain living organisms, and precautions should be adopted to prevent any permanent alteration of the biology (including introduction of alien species) or habitat properties of these environments.
28. Drilling fluids and equipment that will enter the subglacial aquatic environment should be cleaned to the extent practicable, and records should be maintained of sterility tests (e.g., bacterial counts by fluorescence microscopy at the drilling site). As a provisional guideline for general cleanliness, these objects should not contain more microbes than are present in an equivalent volume of the ice that is being drilled through to reach the subglacial environment. This standard should be re-evaluated when new data on subglacial aquatic microbial populations become available".[39]
Blood Falls was used as the target for testing IceMole in November 2014. This is being developed in connection with the Enceladus Explorer (EnEx) project by a team from the FH Aachen in Germany. The test returned a clean subglacial sample from the outflow channel from Blood Falls.[40] Ice Mole navigates through the ice by melting it, also using a driving ice screw, and using differential melting to navigate and for hazard avoidance. It is designed for autonomous navigation to avoid obstacles such as cavities and embedded meteorites, so that it can be deployed remotely on Encladus. It uses no drilling fluids, and can be sterilized to suit the planetary protection requirements as well as the requirements for subglacial exploration. The probe was sterilized to these protocols using hydrogen peroxide and UV sterilization. Also, only the tip of the probe samples the liquid water directly.[34][41]
Qaidam Basin
[edit]
At 4,500 metres (14,800 ft), Qaidam Basin is the plateau with highest average elevation on the Earth. The atmospheric pressure is 50% - 60% of sea level pressures, and as a result of the thin atmosphere it has high levels of UV radiation, and large temperature swings from day to night. Also, the Himalayas to the South block humid air from India, making it hyper arid.
In the most ancient playas (Da Langtang) at the north west of the plateau, the evaporated salts are magnesium sulfates (sulfates are common on Mars). This, combined with the cold and dryness conditions make it an interesting analogue of the Martian salts and salty regolith. An expedition found eight strains of Haloarchaea inhabiting the salts, similar to some species of Virgibacillus, Oceanobacillus, Halobacillus, and Ter-ribacillus.[42]
Mojave Desert
[edit]
The Mojave Desert is a desert within the United States that is often used for testing Mars rovers.[43] It also has useful biological analogues for Mars.
- Some arid conditions and chemical processes are similar to Mars.[2]
- Has extremophiles within the soils.[2]
- Desert varnish similar to Mars.[2][44]
- Carbonate rocks with iron oxide coatings similar to Mars - niche for microbes inside and underneath the rocks, protected from the sun by the iron oxide coating, if microbes existed or exist on Mars they could be protected similarly by the iron oxide coating of rocks there.[45]
Other analogue deserts
[edit]- Namib Desert - oldest desert, life with limited water and high temperatures, large dunes and wind features[2]
- Ibn Battuta Centre Sites, Morocco - several sites in the Sahara desert that are analogues of some of the conditions on present day Mars, and used for testing of ESA rovers and astrobiological studies.[2][46]
Axel Heiberg Island (Canada)
[edit]Two sites of special interest: Colour Peak and Gypsum Hill, two sets of cold saline springs on Axel Heiberg Island that flow with almost constant temperature and flow rate throughout the year. The air temperatures are comparable to the McMurdo Dry Valleys, range -15 °C to -20 °C (for the McMurdo Dry Valleys -15 °C to -40 °C). The island is an area of thick permafrost with low precipitation, leading to desert conditions. The water from the springs has a temperature of between -4 °C and 7 °C. A variety of minerals precipitate out of the springs including gypsum, and at Colour Peak crystals of the metastable mineral ikaite (CaCO
3·6H
2O) which decomposes rapidly when removed from freezing water.[47]
"At these sites permafrost, frigid winter temperatures, and arid atmospheric conditions approximate conditions of present-day, as well as past, Mars. Mineralogy of the three springs is dominated by halite (NaCl), calcite (CaCO
3), gypsum (CaSO
4·2 H2O), thenardite (Na
2SO
4), mirabilite (Na
2SO
4·10H
2O), and elemental sulfur (S°).[48]
Some of the extremophiles from these two sites have been cultured in simulated Martian environment, and it is thought that they may be able to survive in a Martian cold saline spring, if such exist.[49]
Colour Lake Fen
[edit]This is another Mars analogue habitat in Axel Heiberg Island close to Colour Peak and Gypsum Hill. The frozen soil and permafrost hosts many microbial communities that are tolerant of anoxic, acid, saline and cold conditions. Most are in survival rather than colony forming mode. Colour Lake Fen is a good terrestrial analogue of the saline acidic brines that once existed in the Meridani Planum region of Mars and may possibly still exist on the martian surface. Some of the microbes found there are able to survive in Mars-like conditions.[1]
"A martian soil survey in the Meridiani Planum region found minerals indicative of saline acidic brines. Therefore acidic cryosol/permafrost habitats may have once existed and are perhaps still extant on the martian surface. This site comprises a terrestrial analogue for these environments and hosts microbes capable of survival under these Mars-like conditions"[1]
Rio Tinto, Spain
[edit]Rio Tinto is the largest known sulfide deposit in the world, and it is located in the Iberian Pyrite Belt.[50] (IPB).

Many of the extremophiles that live in these deposits are thought to survive independently of the Sun. This area is rich in iron and sulfur minerals such as
- hematite (Fe
2O
3) which is common in the Meridiani Planum area of Mars explored by Opportunity rover and thought to be signs of ancient hot springs on Mars.

- jarosite (KFe3+
3(OH)
6(SO
4)
2), discovered on Mars by Opportunity and on Earth forms either in acid mine drainage, during oxidation of sulphide minerals, and during alteration of volcanic rocks by acidic, sulphur-rich fluids near volcanic vents.[51]
Permafrost soils
[edit]Much of the water on Mars is permanently frozen, mixed with the rocks. So terrestrial permafrosts are a good analogue. And some of the Carnobacterium species isolated from permafrosts have the ability to survive under the conditions of the low atmospheric pressures, low temperatures and CO
2 dominated anoxic atmosphere of Mars.[52]
Ice caves
[edit]Ice caves, or ice preserved under the surface in cave systems protected from the surface conditions, may exist on Mars.[53] The ice caves near the summit of Mount Erebus in Antarctica, are associated with fumaroles in a polar alpine environments starved in organics and with oxygenated hydrothermal circulation in highly reducing host rock.[54][55]
Cave systems
[edit]Mines on Earth give access to deep subsurface environments which turn out to be inhabited, and deep caves may possibly exist on Mars, although without the benefits of an atmosphere.[56]
Basaltic lava tubes
[edit]The only caves found so far on Mars are lava tubes. These are insulated to some extent from surface conditions and may retain ice also when there is none left on the surface, and may have access to chemicals such as hydrogen from serpentization to fuel chemosynthetic life. Lava tubes on Earth have microbial mats, and mineral deposits inhabited by microbes. These are being studied to help with identification of life on Mars if any of the lava tubes there are inhabited.[57][58]
Lechuguilla Cave
[edit]First of the terrestrial sulfur caves to be investigated as a Mars analogue for sulfur based ecosystems that could possibly exist underground also on Mars.[59] On Earth, these form when hydrogen sulfide from below the cave meets the surface oxygenated zone. As it does so, sulfuric acid forms, and microbes accelerate the process.[60]
The high abundance of sulfur on Mars combined with presence of ice, and trace detection of methane suggest the possibility of sulfur caves below the surface of Mars like this.[61]
Cueva de Villa Luz
[edit]The Snottites in the toxic sulfur cave Cueva de Villa Luz flourish on Hydrogen Sulfide gas and though some are aerobes (though only needing low levels of oxygen), some of these species (e.g. Acidianus), like those that live around hydrothermal vents, are able to survive independent of a source of oxygen. So the caves may give insight into subsurface thermal systems on Mars, where caves similar to the Cueva de Villa Luz could occur.[62]
Movile Cave
[edit]- Movile Cave is thought to have been isolated from the atmosphere and sunlight for 5.5 million years.[56]
- Atmosphere rich in H
2S and CO
2 with 1% - 2% CH
4 (methane) - It does have some oxygen, 7-10% O
2 in the cave atmosphere, compared to 21% O
2 in the air - Microbes rely mainly on sulfide and methane oxidation.
- Has 33 vertebrates and a wide range of indigenous microbes.
Magnesium sulfate lakes
[edit]

4·11H
2O. Evidence from orbital measurements show that this is the phase of Magnesium sulfate which would be in equilibrium with the ice in the Martian polar and sub polar regions[63] It also occurs on the Earth, for instance in Basque Lake 2 in Western Columbia, which may give an analogue for Mars habitats.
Opportunity found evidence for magnesium sulfates on Mars (one form of it is epsomite, or "Epsom salts"), in 2004.[64] Curiosity rover has detected calcium sulfates on Mars.[65] Orbital maps also suggest that hydrated sulfates may be common on Mars. The orbital observations are consistent with iron sulfate or a mixture of calcium and magnesium sulfate.[66]
Magnesium sulfate is a likely component of cold brines on Mars, especially with the limited availability of subsurface ice. Terrestrial magnesium sulfate lakes have similar chemical and physical properties. They also have a wide range of halophilic organisms, in all the three Kingdoms of life (Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaryota), in the surface and near subsurface.[67] With the abundance of algae and bacteria, in alkaline hypersaline conditions, they are of astrobiological interest for both past and present life on Mars.
These lakes are most common in western Canada, and the northern part of Washington state, USA. One of the examples, is Basque Lake 2 in Western Canada, which is highly concentrated in magnesium sulfate. In summer it deposits epsomite ("Epsom salts"). In winter, it deposits meridianiite. This is named after Meridiani Planum where Opportunity rover found crystal molds in sulfate deposits (Vugs) which are thought to be remains of this mineral which have since been dissolved or dehydrated. It is preferentially formed at subzero temperatures, and is only stable below 2 °C,[68] while Epsomite (MgSO
4·7H
2O) is favored at higher temperatures.[69][70]
Another example is Spotted Lake, which shows a wide variety of minerals, most of them sulfates, with sodium, magnesium and calcium as cations.
"Dominant minerals included blöedite Na
2Mg(SO
4)
2·4H
2O, konyaite Na
2Mg(SO
4)
2·5H
2O, epsomite MgSO
4·7H
2O, and gypsumCaSO
4·2H
2O, with minor eugsterite, picromerite, syngenite, halite, and sylvite",[71]
Some of the microbes isolated have been able to survive the high concentrations of magnesium sulfates found in Martian soils, also at low temperatures that may be found on Mars.[72][73][74]
Sulfates (for instance of sodium, magnesium and calcium) are also common in other continental evaporates (such as the salars of the Atacama Desert), as distinct from salt beds associated with marine deposits which tend to consist mainly of halites (chlorides).[75]
Subglacial lakes
[edit]
Subglacial lakes such as Lake Vostok may give analogues of Mars habitats beneath ice sheets. Sub glacial lakes are kept liquid partly by the pressure of the depth of ice, but that contributes only a few degrees of temperature rise. The main effect that keeps them liquid is the insulation of the ice blocking escape of heat from the interior of the Earth, similarly to the insulating effect of deep layers of rock. As for deep rock layers, they don't require extra geothermal heating below a certain depth.
In the case of Mars, the depth needed for geothermal melting of the basal area of a sheet of ice is 4-6 kilometers. The ice layers are probably only 3.4 to 4.2 km in thickness for the north polar cap. However, it was shown that the situation is different when considering a lake that is already melted. When they applied their model to Mars, they showed that a liquid layer, once melted (initially open to the surface of the ice), could remain stable at any depth over 600 meters even in absence of extra geothermal heating.[76] According to their model, if the polar regions had a subsurface lake perhaps formed originally through friction as a subglacial lake at times of favourable axial tilt, then supplied by accumulating layers of snow on top as the ice sheets thickened, they suggest that it could still be there. If so, it could be occupied by similar life forms to those that could survive in Lake Vostok.[76]
Ground penetrating radar could detect these lakes because of the high radar contrast between water and ice or rock. MARSIS, the ground penetrating radar on ESA's Mars Express detected a subglacial lake in Mars near the south pole.
Subsurface life kilometers below the surface
[edit]Investigations of life in deep mines, and drilling beneath the ocean depths may give an insight into possibilities for life in the Mars hydrosphere and other deep subsurface habitats, if they exist.
Mponeng gold mine in South Africa
[edit]- bacteria obtain their energy from hydrogen oxidation linked to sulfate reduction, living independent of the surface[56]
- nematodes feeding on those bacteria, again living independent of the surface.
- 3 to 4 km depth
Boulby Mine on the edge of the Yorkshire moors
[edit]- 250 million year halite (chloride) and sulfate salts[56]
- High salinity and low water activity
- 1.1. km depth
- Anaerobic microbes that could survive cut off from the atmosphere
Alpine and permafrost lichens
[edit]In high alpine and polar regions, lichens have to cope with conditions of high UV fluxes low temperatures and arid environments. This is especially so when the two factors, polar regions and high altitudes are combined. These conditions occur in the high mountains of Antarctica, where lichens grow at altitudes up to 2,000 meters with no liquid water, just snow and ice. Researchers described this as the most Mars-like environment on the Earth.[77]
See also
[edit]- Life on Mars – Scientific assessments on the microbial habitability of Mars
- Terrestrial analogue sites – Places on Earth used to mimic extraterrestrial locations
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g The Planetary and Space Sciences Research Institute, The Open University (5 December 2012). "TN2: The Catalogue of Planetary Analogues" (PDF). Under ESA contract: 4000104716/11/NL/AF.
- ^ a b c d e f g Preston, Louisa J.; Dartnell, Lewis R. (2014). "Planetary habitability: lessons learned from terrestrial analogues" (PDF). International Journal of Astrobiology. 13 (1): 81–98. Bibcode:2014IJAsB..13...81P. doi:10.1017/S1473550413000396. ISSN 1473-5504. S2CID 122721110.
- ^ a b Q. Choi, Charles (May 17, 2010). "Mars Contamination Dust-Up". Astrobiology Magazine. Archived from the original on August 20, 2011.
Whenever multiple biocidal factors are combined, the survival rates plummet quickly,
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Dieser, M.; Battista, J. R.; Christner, B. C. (2013). "DNA Double-Strand Break Repair at -15 C". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 79 (24): 7662–7668. doi:10.1128/AEM.02845-13. ISSN 0099-2240. PMC 3837829. PMID 24077718.
- ^ a b Billi, Daniela; Viaggiu, Emanuela; Cockell, Charles S.; Rabbow, Elke; Horneck, Gerda; Onofri, Silvano (2011). "Damage Escape and Repair in DriedChroococcidiopsisspp. from Hot and Cold Deserts Exposed to Simulated Space and Martian Conditions". Astrobiology. 11 (1): 65–73. Bibcode:2011AsBio..11...65B. doi:10.1089/ast.2009.0430. ISSN 1531-1074. PMID 21294638.
- ^ a b "Surviving the conditions on Mars". DLR. 26 April 2012.
- ^ Jean-Pierre de Vera (August 2012). "Lichens as survivors in space and on Mars". Fungal Ecology. 5 (4): 472–479. doi:10.1016/j.funeco.2012.01.008.
- ^ R. de la Torre Noetzel; F.J. Sanchez Inigo; E. Rabbow; G. Horneck; J. P. de Vera; L.G. Sancho. "Survival of lichens to simulated Mars conditions" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-06-03.
- ^ F.J. Sáncheza; E. Mateo-Martíb; J. Raggioc; J. Meeßend; J. Martínez-Fríasb; L.Ga. Sanchoc; S. Ottd; R. de la Torrea (November 2012). "The resistance of the lichen Circinaria gyrosa (nom. provis.) towards simulated Mars conditions—a model test for the survival capacity of an eukaryotic extremophile". Planetary and Space Science. 72 (1): 102–110. Bibcode:2012P&SS...72..102S. doi:10.1016/j.pss.2012.08.005.
- ^ David, Leonard (April 1, 2013). "Has NASA's Curiosity Rover Found Clues to Life's Building Blocks on Mars?". Space.com.
- ^ Brogan, Jacob (April 7, 2015). "Staying Healthy on the Red Planet 338 72 A chemical found in Martian soil might make it more dangerous to establish a permanent settlement there". Slate.
- ^ Encrenaz, T.; Greathouse, T. K.; Lefèvre, F.; Montmessin, F.; Forget, F.; Fouchet, T.; DeWitt, C.; Richter, M. J.; Lacy, J. H.; Bézard, B.; Atreya, S. K. (2015). "Seasonal variations of hydrogen peroxide and water vapor on Mars: Further indications of heterogeneous chemistry". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 578: A127. Bibcode:2015A&A...578A.127E. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201425448. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ Agee, Ernest; Orton, Andrea; Rogers, John (2013). "CO2Snow Deposition in Antarctica to Curtail Anthropogenic Global Warming". Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology. 52 (2): 281–288. Bibcode:2013JApMC..52..281A. doi:10.1175/JAMC-D-12-0110.1. ISSN 1558-8424.
- ^ "Antarctica records unofficial coldest temperature ever". USA Today.
- ^ Cordero, Raul R.; Seckmeyer, Gunther; Damiani, Alessandro; Riechelmann, Stefan; Rayas, Juan; Labbe, Fernando; Laroze, David (2014). "The world's highest levels of surface UV". Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 13 (1): 70–81. doi:10.1039/C3PP50221J. hdl:10533/132342. ISSN 1474-905X. PMID 24202188. S2CID 35887014.
- ^ Wierzchos, Jacek; DiRuggiero, Jocelyne; Vítek, Petr; Artieda, Octavio; Souza-Egipsy, Virginia; Škaloud, Pavel; Tisza, Michel; Davila, Alfonso F.; Vílchez, Carlos; Garbayo, Inés; Ascaso, Carmen (2015). "Adaptation strategies of endolithic chlorophototrophs to survive the hyperarid and extreme solar radiation environment of the Atacama Desert". Frontiers in Microbiology. 6: 934. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00934. ISSN 1664-302X. PMC 4564735. PMID 26441871.
- ^ a b c d Azua-Bustos, Armando; Caro-Lara, Luis; Vicuña, Rafael (2015). "Discovery and microbial content of the driest site of the hyperarid Atacama Desert, Chile". Environmental Microbiology Reports. 7 (3): 388–394. doi:10.1111/1758-2229.12261. ISSN 1758-2229. PMID 25545388.
- ^ a b Williams, Andrew (May 18, 2015). "Driest Place on Earth Hosts Life". NASA Astrobiology Magazine (online). NASA.
- ^ a b Parro, Victor; de Diego-Castilla, Graciela; Moreno-Paz, Mercedes; Blanco, Yolanda; Cruz-Gil, Patricia; Rodríguez-Manfredi, José A.; et al. (2011). "A Microbial Oasis in the Hypersaline Atacama Subsurface Discovered by a Life Detector Chip: Implications for the Search for Life on Mars". Astrobiology. 11 (10): 969–996. Bibcode:2011AsBio..11..969P. doi:10.1089/ast.2011.0654. ISSN 1531-1074. PMC 3242637. PMID 22149750.
- ^ The Planetary and Space Sciences Research Institute, The Open University (5 December 2012). "TN2: The Catalogue of Planetary Analogues, section 2.6.1" (PDF). Under ESA contract: 4000104716/11/NL/AF.
- ^ "Microbial oasis discovered beneath the Atacama Desert" (Public release). FECYT - Spanish Foundation for Science and Technology. 16 February 2012.
- ^ "Mars rover tests driving, drilling and detecting life in Chile's high desert". Nasa Astrobiology Magazine. Mar 17, 2017.
- ^ "NASA Tests Life-Detection Drill in Earth's Driest Place". NASA Press Release. February 26, 2016.
- ^ a b Azua-Bustos, Armando; Urrejola, Catalina; Vicuña, Rafael (2012). "Life at the dry edge: Microorganisms of the Atacama Desert". FEBS Letters. 586 (18): 2939–2945. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.07.025. ISSN 0014-5793. PMID 22819826.
- ^ a b Osano, A., and A. F. Davila (2014). "Analysis of Photosynthetic Activity of Cyanobacteria Inhabiting Halite Evaporites of Atacama Desert, Chile" (PDF). Lunar and Planetary Institute Science Conference Abstracts. 45 (1777): 2919. Bibcode:2014LPI....45.2919O.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bortman, Henry (Jun 22, 2006). "Journey to Yungay". Astrobiology Magazine (NASA).
- ^ Wierzchos, J.; Davila, A. F.; Sánchez-Almazo, I. M.; Hajnos, M.; Swieboda, R.; Ascaso, C. (2012). "Novel water source for endolithic life in the hyperarid core of the Atacama Desert". Biogeosciences. 9 (6): 2275–2286. Bibcode:2012BGeo....9.2275W. doi:10.5194/bg-9-2275-2012. ISSN 1726-4189.
- ^ N. Hoffman and P. R. Kyle (2003). The Ice Towers of Mt. Erebus as analogues of biological refuges on Mars. Sixth International Conference on Mars.
- ^ McKay, Christopher P. (2008). "Snow recurrence sets the depth of dry permafrost at high elevations in the McMurdo Dry Valleys of Antarctica". Antarctic Science. 21 (1): 89. doi:10.1017/S0954102008001508. ISSN 0954-1020. S2CID 129096753.
- ^ The Planetary and Space Sciences Research Institute, The Open University (December 5, 2012). "TN2: The Catalogue of Planetary Analogues, section 1.6.3" (PDF). Under ESA contract: 4000104716/11/NL/AF.
- ^ Dickson, James L.; Head, James W.; Levy, Joseph S.; Marchant, David R. (2013). "Don Juan Pond, Antarctica: Near-surface CaCl2-brine feeding Earth's most saline lake and implications for Mars". Scientific Reports. 3: 1166. Bibcode:2013NatSR...3E1166D. doi:10.1038/srep01166. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 3559074. PMID 23378901.
- ^ Stacey, Kevin (February 7, 2013). "How the world's saltiest pond gets its salt - describing the research of Jay Dickson and Jim Head".
- ^ a b Dachwald, Bernd; Mikucki, Jill; Tulaczyk, Slawek; Digel, Ilya; Espe, Clemens; Feldmann, Marco; Francke, Gero; Kowalski, Julia; Xu, Changsheng (2014). "IceMole: a maneuverable probe for clean in situ analysis and sampling of subsurface ice and subglacial aquatic ecosystems". Annals of Glaciology. 55 (65): 14–22. Bibcode:2014AnGla..55...14D. doi:10.3189/2014AoG65A004. ISSN 0260-3055.
- ^ a b c Grom, Jackie (April 16, 2009). "Ancient Ecosystem Discovered Beneath Antarctic Glacier". Science. Retrieved April 17, 2009.
- ^ Mikucki, Jill A.; Pearson, Ann; Johnston, David T.; Turchyn, Alexandra V.; Farquhar, James; et al. (April 17, 2009). "A Contemporary Microbially Maintained Subglacial Ferrous "Ocean"". Science. 324 (5925): 397–400. Bibcode:2009Sci...324..397M. doi:10.1126/science.1167350. PMID 19372431. S2CID 44802632.
- ^ "Science Goal 1: Determine if Life Ever Arose On Mars". Mars Exploration Program. NASA. Retrieved October 17, 2010.
- ^ "The Case of the Missing Mars Water". Science@NASA. NASA. January 5, 2001. Retrieved April 20, 2009.
- ^ "SCAR's code of conduct for the exploration and research of subglacial aquatic environments" (PDF). XXXIV Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting, Buenos Aires, June 20th - July 1st 2011.
- ^ Brabaw, Kasandra (April 7, 2015). "IceMole Drill Built to Explore Saturn's Icy Moon Enceladus Passes Glacier Test". Space.com.
- ^ ANDERSON, PAUL SCOTT (February 29, 2012). "Exciting New 'Enceladus Explorer' Mission Proposed to Search for Life". Universe Today.
- ^ Wang, A., et al. "Saline Playas on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau as Mars Analog for the Formation-Preservation of Hydrous Salts and Biosignatures." AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts. Vol. 1. 2010.
- ^ "Mojave Desert Tests Prepare for NASA Mars Roving".
- ^ Salas, E., et al. "The Mojave Desert: A Martian Analog Site for Future Astrobiology Themed Missions." LPI Contributions 1612 (2011): 6042.
- ^ Bishop, Janice L.; Schelble, Rachel T.; McKay, Christopher P.; Brown, Adrian J.; Perry, Kaysea A. (2011). "Carbonate rocks in the Mojave Desert as an analogue for Martian carbonates". International Journal of Astrobiology. 10 (4): 349–358. Bibcode:2011IJAsB..10..349B. doi:10.1017/S1473550411000206. ISSN 1473-5504. S2CID 122114343.
- ^ "Ibn Battuta Centre - activities on Mars analogue sites". Archived from the original on 2015-04-18.
- ^ Impey, Chris, Jonathan Lunine, and José Funes, eds. Frontiers of astrobiology (page 161). Cambridge University Press, 2012.
- ^ Battler, Melissa M.; Osinski, Gordon R.; Banerjee, Neil R. (2013). "Mineralogy of saline perennial cold springs on Axel Heiberg Island, Nunavut, Canada and implications for spring deposits on Mars". Icarus. 224 (2): 364–381. Bibcode:2013Icar..224..364B. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2012.08.031. ISSN 0019-1035.
- ^ The Planetary and Space Sciences Research Institute, The Open University (5 December 2012). "TN2: The Catalogue of Planetary Analogues, section 4.6.1" (PDF). Under ESA contract: 4000104716/11/NL/AF.
- ^ Gronstal, Aaron L. (2014-07-24). "Biomarkers of the Deep". AstroBiology Magazine (NASA).
- ^ Elwood Madden, M. E.; Bodnar, R. J.; Rimstidt, J. D. (2004). "Jarosite as an indicator of water-limited chemical weathering on Mars". Nature. 431 (7010): 821–823. Bibcode:2004Natur.431..821M. doi:10.1038/nature02971. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 15483605. S2CID 10965423.
- ^ Nicholson, Wayne, et al. "Isolation of bacteria from Siberian permafrost capable of growing under simulated Mars atmospheric pressure and composition." 40th COSPAR Scientific Assembly. Held 2–10 August 2014, in Moscow, Russia, Abstract F3. 3-10-14.. Vol. 40. 2014.
- ^ Williams, K.E.; McKay, Christopher P.; Toon, O.B.; Head, James W. (2010). "Do ice caves exist on Mars?" (PDF). Icarus. 209 (2): 358–368. Bibcode:2010Icar..209..358W. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2010.03.039. ISSN 0019-1035. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-10-08. Retrieved 2017-03-01.
- ^ Wall, Mike (9 December 2011). "Antarctic Cave Microbes Shed Light on Life's Diversity". Livescience.
- ^ Tebo, Bradley M.; Davis, Richard E.; Anitori, Roberto P.; Connell, Laurie B.; Schiffman, Peter; Staudigel, Hubert (2015). "Microbial communities in dark oligotrophic volcanic ice cave ecosystems of Mt. Erebus, Antarctica". Frontiers in Microbiology. 6: 179. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00179. ISSN 1664-302X. PMC 4356161. PMID 25814983.
- ^ a b c d Aerts, Joost; Röling, Wilfred; Elsaesser, Andreas; Ehrenfreund, Pascale (2014). "Biota and Biomolecules in Extreme Environments on Earth: Implications for Life Detection on Mars". Life. 4 (4): 535–565. Bibcode:2014Life....4..535A. doi:10.3390/life4040535. ISSN 2075-1729. PMC 4284457. PMID 25370528.
- ^ Northup, D.E.; Melim, L.A.; Spilde, M.N.; Hathaway, J.J.M.; Garcia, M.G.; Moya, M.; Stone, F.D.; Boston, P.J.; Dapkevicius, M.L.N.E.; Riquelme, C. (2011). "Lava Cave Microbial Communities Within Mats and Secondary Mineral Deposits: Implications for Life Detection on Other Planets". Astrobiology. 11 (7): 601–618. Bibcode:2011AsBio..11..601N. doi:10.1089/ast.2010.0562. ISSN 1531-1074. PMC 3176350. PMID 21879833.
- ^ Northup, Diana E.; et al. (2012). "Life in Earth's Lava Caves: Implications for Life Detection on Other Planets". Life on Earth and other Planetary Bodies. Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology. Vol. 24. Springer Netherlands. pp. 459–484. Bibcode:2012leop.book..459N. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-4966-5_26. ISBN 9789400749665.
- ^ Nadis, Steve (1997). "Looking inside earth for life on Mars". Technology Review. 100 (8): 14–16. Archived from the original on April 18, 2015. Retrieved March 1, 2017.
- ^ E. Northup, Kathleen H. Lavoie, Diana (2001). "Geomicrobiology of Caves: A Review". Geomicrobiology Journal. 18 (3): 199–222. doi:10.1080/01490450152467750. ISSN 0149-0451. S2CID 216641346. Retrieved December 19, 2020.
- ^ Boston, Penelope J.; Hose, Louise D.; Northup, Diana E.; Spilde, Michael N. (2006). The microbial communities of sulfur caves: A newly appreciated geologically driven system on Earth and potential model for Mars. Vol. 404: Perspectives on Karst Geomorphology, Hydrology, and Geochemistry - A Tribute Volume to Derek C. Ford and William B. White. pp. 331–344. doi:10.1130/2006.2404(28). ISBN 978-0813724041.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Hose, Louise D.; Palmer, Arthur N.; Palmer, Margaret V.; Northup, Diana E.; Boston, Penelope J.; DuChene, Harvey R. (2000). "Microbiology and geochemistry in a hydrogen-sulphide-rich karst environment" (PDF). Chemical Geology. 169 (3–4): 399–423. Bibcode:2000ChGeo.169..399H. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00217-5. ISSN 0009-2541. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2017-03-01.
- ^ Peterson, R.C.; Nelson, W.; Madu, B.; Shurvell, H.F. (2007). "Meridianiite: A new mineral species observed on Earth and predicted to exist on Mars". American Mineralogist. 92 (10): 1756–1759. Bibcode:2007AmMin..92.1756P. doi:10.2138/am.2007.2668. ISSN 0003-004X. S2CID 128695637.
- ^ Bortman, Henry (Mar 3, 2004). "Evidence of Water Found on Mars". Astrobiology Magazine (NASA).
- ^ Nachon, M.; Clegg, S. M.; Mangold, N.; Schröder, S.; Kah, L. C.; Dromart, G.; Ollila, A.; Johnson, J. R.; Oehler, D. Z.; Bridges, J. C.; Le Mouélic, S.; Forni, O.; Wiens, R.C.; Anderson, R. B.; Blaney, D. L.; Bell, J.F.; Clark, B.; Cousin, A.; Dyar, M. D.; Ehlmann, B.; Fabre, C.; Gasnault, O.; Grotzinger, J.; Lasue, J.; Lewin, E.; Léveillé, R.; McLennan, S.; Maurice, S.; Meslin, P.-Y.; Rapin, W.; Rice, M.; Squyres, S. W.; Stack, K.; Sumner, D. Y.; Vaniman, D.; Wellington, D. (2014). "Calcium sulfate veins characterized by ChemCam/Curiosity at Gale crater, Mars". Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 119 (9): 1991–2016. Bibcode:2014JGRE..119.1991N. doi:10.1002/2013JE004588. ISSN 2169-9097. S2CID 32976900.
- ^ Palus, Shannon (2015). "Water Beneath the Surface of Mars, Bound Up in Sulfates". Eos. 96. doi:10.1029/2015EO027799. ISSN 2324-9250.
- ^ Foster, Ian S.; King, Penelope L.; Hyde, Brendt C.; Southam, Gordon (2010). "Characterization of halophiles in natural MgSO
4 salts and laboratory enrichment samples: Astrobiological implications for Mars". Planetary and Space Science. 58 (4): 599–615. Bibcode:2010P&SS...58..599F. doi:10.1016/j.pss.2009.08.009. ISSN 0032-0633. - ^ "An Earth and Mars mineral – Meridianiite MgSO4.11H2O". Crystallography 365. July 30, 2014.
- ^ Marion, G.M.; Catling, D.C.; Zahnle, K.J.; Claire, M.W. (2010). "Modeling aqueous perchlorate chemistries with applications to Mars". Icarus. 207 (2): 675–685. Bibcode:2010Icar..207..675M. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2009.12.003. ISSN 0019-1035.
- ^ "Meridianiite Mineral Data". webmineral.com. Retrieved March 2, 2017.
- ^ K. M. Cannon; L. A. Fenwick; R. C. Peterson (2012). "Spotted Lake: Mineralogical Clues for the Formation of Authigenic Sulfates in Ancient Lakes on Mars" (PDF). Lunar and Planetary Institute Science Conference Abstracts. 43 (1659): 1989. Bibcode:2012LPI....43.1989C.
- ^ Kilmer, Brian R.; Eberl, Timothy C.; Cunderla, Brent; Chen, Fei; Clark, Benton C.; Schneegurt, Mark A. (2014). "Molecular and phenetic characterization of the bacterial assemblage of Hot Lake, WA, an environment with high concentrations of magnesium sulphate, and its relevance to Mars". International Journal of Astrobiology. 13 (1): 69–80. Bibcode:2014IJAsB..13...69K. doi:10.1017/S1473550413000268. ISSN 1473-5504. PMC 3989109. PMID 24748851.
- ^ Crisler, J.D.; Newville, T.M.; Chen, F.; Clark, B.C.; Schneegurt, M.A. (2012). "Bacterial Growth at the High Concentrations of Magnesium Sulfate Found in Martian Soils". Astrobiology. 12 (2): 98–106. Bibcode:2012AsBio..12...98C. doi:10.1089/ast.2011.0720. ISSN 1531-1074. PMC 3277918. PMID 22248384.
- ^ "Searching salt for answers about life on Earth, Mars". Science Daily - press release from Wichita State University. August 9, 2012.
- ^ Barbieri, Roberto; Stivaletta, Nunzia (2011). "Continental evaporites and the search for evidence of life on Mars". Geological Journal. 46 (6): 513–524. doi:10.1002/gj.1326. ISSN 0072-1050. S2CID 140151668.
- ^ a b Duxbury, N. S.; Zotikov, I. A.; Nealson, K. H.; Romanovsky, V. E.; Carsey, F. D. (2001). "A numerical model for an alternative origin of Lake Vostok and its exobiological implications for Mars". Journal of Geophysical Research. 106 (E1): 1453–1462. Bibcode:2001JGR...106.1453D. doi:10.1029/2000JE001254. ISSN 0148-0227.
- ^ de Vera, Jean-Pierre; Schulze-Makuch, Dirk; Khan, Afshin; Lorek, Andreas; Koncz, Alexander; Möhlmann, Diedrich; Spohn, Tilman (2014). "Adaptation of an Antarctic lichen to Martian niche conditions can occur within 34 days". Planetary and Space Science. 98: 182–190. Bibcode:2014P&SS...98..182D. doi:10.1016/j.pss.2013.07.014. hdl:2376/5829. ISSN 0032-0633.