User:The wub/Portal
| Highlights | Explore | Get involved |

The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (usually shortened to the United Kingdom, the UK or - informally - Britain) is a country and sovereign state lying north-west of the continent of Europe. It occupies all of the island of Great Britain and the north-east of the island of Ireland, sharing a border with the Republic of Ireland. The United Kingdom is bounded by the Atlantic Ocean, and its ancillary bodies of water, including the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea, St George's Channel, and the Irish Sea. It is linked to France and Continental Europe by the Channel Tunnel.
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy composed of four constituent countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The current monarch is Queen Elizabeth II, who is also the Queen and Head of State of fifteen other Commonwealth Realms, including Canada, Australia and New Zealand. The Crown Dependencies of the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man form a federacy with the United Kingdom collectively known as the British Islands. The UK also has fourteen overseas territories, remnants of the British Empire which at its height encompassed a quarter of the world's surface and population.
Although Britain was the foremost great power during the 19th century, and a superpower in the early 20th, the economic cost of two world wars and the decline of its empire in the latter half of the 20th century diminished its status in global affairs. However, as a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, a nuclear power, a member of the G8, the world's fifth largest economy, and having the third highest defence spending, the UK remains an important political, economic and military world power. It is a member of the European Union and the Commonwealth of Nations.
Featured article
The Rolls-Royce R was a British aero engine designed and built specifically for air racing purposes by Rolls-Royce Limited. Developed from the Rolls-Royce Buzzard, it was a 37-litre (2,240 cu in) capacity, supercharged V-12 capable of producing just under 2,800 horsepower (2,090 kW), and weighed 1,640 pounds (770 kg). Factory testing initially revealed mechanical failures that were reduced by the use of redesigned components, greatly improving reliability. The R was highly successful during its use in the Schneider Trophy seaplane competitions held in England in 1929 and 1931. Shortly after the 1931 competition, an R engine using a special fuel blend powered the winning Supermarine S.6B aircraft to a new airspeed record of over 400 miles per hour (640 km/h). Continuing through the 1930s, both new and used R engines were used to achieve various land and water speed records by such racing personalities as Sir Henry Segrave, Sir Malcolm Campbell, and his son Donald; the last record was set in 1939. Nineteen R engines were assembled in a limited production run between 1929 and 1931. The experience gained by Rolls-Royce and Supermarine designers was invaluable in the subsequent development of the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine and the Spitfire. (Full article...)
Featured biography
Charles Darwin was an English naturalist who proposed and provided evidence for the theory that all species have evolved over time from a common ancestor through the process of natural selection. This theory came to be accepted by the scientific community in modified form, forming much of the basis of modern evolutionary theory, a cornerstone of biology. His five-year voyage on the Beagle established him as a prominent geologist whose observations and theories supported uniformitarianism. Puzzled by the geographical distribution of wildlife and fossils he collected on the voyage, Darwin investigated the transmutation of species and conceived his theory of natural selection in 1838. In 1858, Alfred Russel Wallace sent him an essay describing a similar theory, causing the two to publish their theories in a joint publication. His 1859 book On the Origin of Species established evolution by common descent as the dominant scientific explanation of the diversity of life in nature. (Full article...)
Did you know...
Featured picture
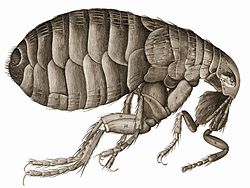
Robert Hooke's drawing of a flea in his Micrographia, a book of observations through various lenses published in 1644. The book demonstrated the tremendous power of the new microscope. On completing the book, Samuel Pepys described it as: "the most ingenious book that I ever read in my life."